Chemosensitizing Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Inducing Apoptosis and Modulating Expression of Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio and Caspases
- PMID: 28124680
- PMCID: PMC5291085
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.903170
Chemosensitizing Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Inducing Apoptosis and Modulating Expression of Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio and Caspases
Abstract
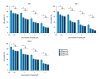
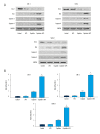
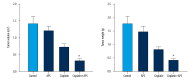
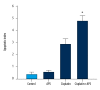
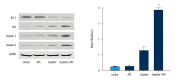
BACKGROUND Platinum-based chemotherapy is the most effective regimen for nasopharyngeal carcinoma, which presents highly invasive and metastatic activity. However, the dose-related toxicity of chemotherapy agents limits the dose administration. Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) is the major active ingredient extracted from Chinese herb Radix Astragali and is proven to be active against carcinomas. We aimed to assess the chemosensitizing effects of Astragalus polysaccharides on nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo and to explore the underlying mechanism. MATERIAL AND METHODS We used BALB/c nu/nu mice and human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines CNE-1, CNE-2, and SUNE-1. MTT, Annexin V/PI, Western blot analysis, and TUNEL assay were carried out. RESULTS APS significantly promoted anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of cisplatin on nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. APS also enhanced the anti-tumor effects and cisplatin-induced apoptosis in the xenograft model. The level of Bcl-2 decreased, while the levels of Bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9 increased in cisplatin combined with APS treatment compared to cisplatin only treatment. The ratio of Bax to Bcl-2 was significantly enhanced by the APS to cisplatin. CONCLUSIONS APS enhanced the anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of cisplatin by modulating expression of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspases on nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and in the xenograft model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

