Isolation and Characterization of a Phaseolus vulgaris Trypsin Inhibitor with Antiproliferative Activity on Leukemia and Lymphoma Cells
- PMID: 28125005
- PMCID: PMC6155916
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22010187
Isolation and Characterization of a Phaseolus vulgaris Trypsin Inhibitor with Antiproliferative Activity on Leukemia and Lymphoma Cells
Abstract
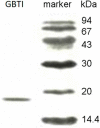
A 17.5-kDa trypsin inhibitor was purified from Phaseolus vulgaris cv. "gold bean" with an isolation protocol including ion exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose (Diethylaminoethyl-cellulose), affinity chromatography on Affi-gel blue gel, ion exchange chromatography on SP-sepharose (Sulfopropyl-sepharose), and gel filtration by FPLC (Fast protein liquid chromatography) on Superdex 75. It dose-dependently inhibited trypsin with an IC50 value of 0.4 μM, and this activity was reduced in the presence of dithiothreitol in a dose- and time-dependent manner, signifying the importance of the disulfide linkage to the activity. It inhibited [methyl-³H] thymidine incorporation by leukemia L1210 cells and lymphoma MBL2 cells with an IC50 value of 2.3 μM and 2.5 μM, respectively. The inhibitor had no effect on fungal growth and the activities of various viral enzymes when tested up to 100 μM.
Keywords: leguminous seeds; leukemia L1210; lymphoma MBL2; purification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Trypsin isoinhibitors with antiproliferative activity toward leukemia cells from Phaseolus vulgaris cv "White Cloud Bean".J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:219793. doi: 10.1155/2010/219793. Epub 2010 Jun 14. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20617140 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of a Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitor with antiproliferative activity from Gymnocladus chinensis (Yunnan bean) seeds.Protein J. 2011 Apr;30(4):240-6. doi: 10.1007/s10930-011-9325-1. Protein J. 2011. PMID: 21468674 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of an antifungal peptide with antiproliferative activity from seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris cv. 'Spotted Bean'.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Feb;74(1):125-30. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0650-9. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17177050
-
A thermostable trypsin inhibitor with antiproliferative activity from small pinto beans.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2014 Aug;29(4):485-90. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2013.805756. Epub 2013 Jul 16. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 23859150
-
Trypsin inhibitors: promising candidate satietogenic proteins as complementary treatment for obesity and metabolic disorders?J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):405-419. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1542387. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30734596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Investigation of Bioactive Compounds from White Kidney Beans (Fruits of Phaseolus multiflorus var. Albus): Identification of Denatonium with Osteogenesis-Inducing Effect.Plants (Basel). 2021 Oct 17;10(10):2205. doi: 10.3390/plants10102205. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34686012 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction, Modification and Biomedical Application of Agarose Hydrogels: A Review.Mar Drugs. 2023 May 14;21(5):299. doi: 10.3390/md21050299. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37233493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mahoney W.C., Hermodson M.A., Jones B., Powers D.D., Corfman R.S., Reeck G.R. Amino acid sequence and secondary structural analysis of the corn inhibitor of trypsin and activated hageman factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1984;259:8412–8416. - PubMed
-
- Telang M., Srinivasan A., Patankar A., Harsulkar A., Joshi V., Damle A., Deshpande V., Sainani M., Ranjekar P., Gupta G., et al. Bitter gourd proteinase inhibitors: Potential growth inhibitors of helicoverpa armigera and spodoptera litura. Phytochemistry. 2003;63:643–652. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00239-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

