Mutations of the LIM protein AJUBA mediate sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to treatment with cell-cycle inhibitors
- PMID: 28126323
- PMCID: PMC5404895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.024
Mutations of the LIM protein AJUBA mediate sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to treatment with cell-cycle inhibitors
Abstract
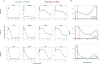
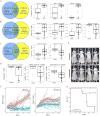
The genomic alterations identified in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumors have not resulted in any changes in clinical care, making the development of biomarker-driven targeted therapy for HNSCC a major translational gap in knowledge. To fill this gap, we used 59 molecularly characterized HNSCC cell lines and found that mutations of AJUBA, SMAD4 and RAS predicted sensitivity and resistance to treatment with inhibitors of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1), checkpoint kinases 1 and 2, and WEE1. Inhibition or knockdown of PLK1 led to cell-cycle arrest at the G2/M transition and apoptosis in sensitive cell lines and decreased tumor growth in an orthotopic AJUBA-mutant HNSCC mouse model. AJUBA protein expression was undetectable in most AJUBA-mutant HNSCC cell lines, and total PLK1 and Bora protein expression were decreased. Exogenous expression of wild-type AJUBA in an AJUBA-mutant cell line partially rescued the phenotype of PLK1 inhibitor-induced apoptosis and decreased PLK1 substrate inhibition, suggesting a threshold effect in which higher drug doses are required to affect PLK1 substrate inhibition. PLK1 inhibition was an effective therapy for HNSCC in vitro and in vivo. However, biomarkers to guide such therapy are lacking. We identified AJUBA, SMAD4 and RAS mutations as potential candidate biomarkers of response of HNSCC to treatment with these mitotic inhibitors.
Keywords: AJUBA; CHK1; Head neck squamous cell carcinoma; Polo-like kinase 1; WEE1.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inactivation enhances PI3K inhibition-mediated apoptosis of NOTCH1-mutant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2025 Aug 10;625:217814. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217814. Epub 2025 May 22. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40412794
-
Small molecule inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 by volasertib (BI 6727) causes significant melanoma growth delay and regression in vivo.Cancer Lett. 2017 Jan 28;385:179-187. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.025. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 27793694 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Cellular Effects of Plk1 Inhibitors Targeting the ATP-binding Domain or Polo-box Domain.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Dec;230(12):3057-67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25042. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25975351
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2011 Jun 15;207(6):337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2011. PMID: 21531084 Review.
-
Polo-like Kinase 1 as an emerging drug target: structure, function and therapeutic implications.J Drug Target. 2021 Feb;29(2):168-184. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2020.1818760. Epub 2020 Sep 14. J Drug Target. 2021. PMID: 32886539 Review.
Cited by
-
Eya2 Is Overexpressed in Human Prostate Cancer and Regulates Docetaxel Sensitivity and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential through AKT/Bcl-2 Signaling.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jun 16;2019:3808432. doi: 10.1155/2019/3808432. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31317026 Free PMC article.
-
Novel DNA targeted therapies for head and neck cancers: clinical potential and biomarkers.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 16;8(46):81662-81678. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20953. eCollection 2017 Oct 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29113422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic characterization of human papillomavirus-positive and -negative human squamous cell cancer cell lines.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 21;8(49):86369-86383. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21174. eCollection 2017 Oct 17. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29156801 Free PMC article.
-
Ajuba Overexpression Promotes Breast Cancer Chemoresistance and Glucose Uptake through TAZ-GLUT3/Survivin Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Feb 7;2022:3321409. doi: 10.1155/2022/3321409. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35178446 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical cMet regulation by vimentin mediates Plk1 inhibitor-induced apoptosis.EMBO Mol Med. 2019 May;11(5):e9960. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201809960. EMBO Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31040125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Broad Institute Picard. http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/
-
- Broad Institute TCGA Genome Data Analysis Center. Mutation Analysis MutSig 2CV v3.1. Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; 2016.
-
- Abe Y, Ohsugi M, Haraguchi K, Fujimoto J, Yamamoto T. LATS2-Ajuba complex regulates gamma-tubulin recruitment to centrosomes and spindle organization during mitosis. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:782–788. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal N, Frederick MJ, Pickering CR, Bettegowda C, Chang K, Li RJ, Fakhry C, Xie TX, Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang N, El-Naggar AK, Jasser SA, Weinstein JN, Trevino L, Drummond JA, Muzny DM, Wu Y, Wood LD, Hruban RH, Westra WH, Koch WM, Califano JA, Gibbs RA, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE, Papadopoulos N, Wheeler DA, Kinzler KW, Myers JN. Exome sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma reveals inactivating mutations in NOTCH1. Science. 2011;333:1154–1157. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai M, Ni J, Wu J, Wang B, Shen S, Yu L. A novel mechanism for activation of Aurora-A kinase by Ajuba. Gene. 2014;543:133–139. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

