Improved outcomes for newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis between 2000 and 2014: cracking the glass ceiling of early death
- PMID: 28126928
- PMCID: PMC5391625
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-11-751628
Improved outcomes for newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis between 2000 and 2014: cracking the glass ceiling of early death
Abstract
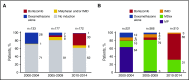
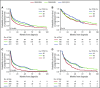
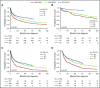
In light of major advances in immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis, we evaluated the trends in presentation, management, and outcome among 1551 newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis patients seen in our institution from 2000 to 2014. As compared with the 2 intervals 2000-2004 and 2005-2009, patients diagnosed in 2010-2014 were less likely to have >2 involved organs. Utilization of autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) was similar across all periods, about one-third of patients, but there was an increase in the use of pre-ASCT bortezomib induction and of unattenuated melphalan conditioning in 2010-2014 compared with earlier periods. Non-ASCT first-line regimen changed with 65% of patients in 2010-2014 received bortezomib-based therapy, 79% of patients in 2005-2009 received melphalan-dexamethasone, and 64% of patients in 2000-2004 received melphalan-prednisone. The rate of better than very good partial response (VGPR) was higher in more recent periods (66% vs 58% vs 51%; P = .001), a change largely driven by improved VGPR rates in the non-ASCT population. Overall survival (OS) has improved, with inflection points for improvement differing for the ASCT and non-ASCT groups. In the ASCT population, the greatest gains were after 2010 (4-year OS, 91% compared with 73% and 65%). In the non-ASCT group, greatest gains were after 2005 (4-year OS, 38%, 32%, and 16%). Fewer patients died within 6 months of diagnosis in the 2 later periods (24% vs 25% vs 37%; P < .001). Overall, outcomes among patients with AL amyloidosis have improved with earlier diagnosis, higher rates of VGPR, lower early mortality, and improved OS.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Breaking bad…proteins.Blood. 2017 Apr 13;129(15):2041-2042. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-02-765560. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28408417 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Hayman SR. Amyloidosis: diagnosis and management. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2005;6(3):208-219. - PubMed
-
- Palladini G, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, et al. New criteria for response to treatment in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis based on free light chain measurement and cardiac biomarkers: impact on survival outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(36):4541-4549. - PubMed
-
- Vrana JA, Gamez JD, Madden BJ, Theis JD, Bergen HR III, Dogan A. Classification of amyloidosis by laser microdissection and mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis in clinical biopsy specimens. Blood. 2009;114(24):4957-4959. - PubMed
-
- Majolino I, Marceno R, Pecoraro G, et al. High-dose therapy and autologous transplantation in amyloidosis-AL. Haematologica. 1993;78(1):68-71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

