Axillobifemoral bypass: a brief surgical and historical review
- PMID: 28127271
- PMCID: PMC5260814
- DOI: 10.23861/ejbm201631744
Axillobifemoral bypass: a brief surgical and historical review
Abstract
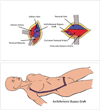
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) occurs when plaque accumulates in the arterial system and obstructs blood flow. Narrowing of the abdominal aorta and the common iliac arteries due to atherosclerotic plaques restricts blood supply to the lower limbs. Clinically, the lower limb symptoms of PAD are intermittent claudication, discoloration of the toes, and skin ulcers, all due to arterial insufficiency. Surgical revascularization is the primary mode of treatment for patients with severe limb ischemia. The objective of the surgical procedure is to bypass a blockage in an occluded major vessel by constructing an alternate route for blood flow using an artificial graft. This article presents information on aortoiliac reconstruction, with an emphasis on axillobifemoral bypass grafting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have completed and submitted the IDMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Blaisdell FW, Demattei GA, Gauder PJ. Extraperitoneal thoracic aorta to femoral bypass graft as replacement for an infected aortic bifurcation prosthesis. Am J Surg. 1961;102:583–585. - PubMed
-
- Blaisdell FW, Hall AD. Axillary-Femoral Artery Bypass for Lower Extremity Ischemia. Surgery. 1963;54:563–568. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
