MiR-222 in Cardiovascular Diseases: Physiology and Pathology
- PMID: 28127557
- PMCID: PMC5239839
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4962426
MiR-222 in Cardiovascular Diseases: Physiology and Pathology
Abstract
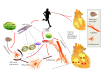
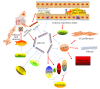
MicroRNAs (miRNAs and miRs) are endogenous 19-22 nucleotide, small noncoding RNAs with highly conservative and tissue specific expression. They can negatively modulate target gene expressions through decreasing transcription or posttranscriptional inducing mRNA decay. Increasing evidence suggests that deregulated miRNAs play an important role in the genesis of cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, circulating miRNAs can be biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. MiR-222 has been reported to play important roles in a variety of physiological and pathological processes in the heart. Here we reviewed the recent studies about the roles of miR-222 in cardiovascular diseases. MiR-222 may be a potential cardiovascular biomarker and a new therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of miR-214 in cardiovascular diseases.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 5;816:138-145. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.08.009. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28842125 Review.
-
MicroRNAs Mediate Beneficial Effects of Exercise in Heart.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1000:261-280. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4304-8_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29098626 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MicroRNA in cardiovascular biology and disease.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017 Aug;26(5):865-874. doi: 10.17219/acem/62915. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 29068585 Review.
-
Roles of miR-17-92 Cluster in Cardiovascular Development and Common Diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9102909. doi: 10.1155/2017/9102909. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28164128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-Analysis of Differential miRNA Expression after Bariatric Surgery.J Clin Med. 2019 Aug 15;8(8):1220. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081220. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31443156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs regulate acute transcriptional changes in broiler embryos in response to modification of incubation temperature.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 27;8(1):11371. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29316-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30054505 Free PMC article.
-
Amniotic Fluid microRNA in Severe Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome Cardiomyopathy-Identification of Differences and Predicting Demise.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Jan 23;9(2):37. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9020037. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 35200691 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of structured exercise training on miRNA expression in previously sedentary individuals.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 18;19(12):e0314281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314281. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39693276 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA MIAT regulates ox-LDL-induced cell proliferation, migration and invasion by miR-641/STIM1 axis in human vascular smooth muscle cells.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 May 20;21(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02048-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34016053 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

