Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 28127589
- PMCID: PMC5260818
Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration
Abstract
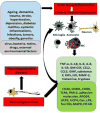
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and Multiple Sclerosis (MS) are characterized by neuronal degeneration and neuronal death in specific regions of the central nervous system (CNS). In AD, neurons of the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex are the first to degenerate, whereas in PD, dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra degenerate. MS patients show destruction of the myelin sheath. Once the CNS neurons are damaged, they are unable to regenerate unlike any other tissue in the body. Neurodegeneration is mediated by inflammatory and neurotoxic mediators such as interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-8, IL-33, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2), CCL5, matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs), granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), glia maturation factor (GMF), substance P, reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), mast cells-mediated histamine and proteases, protease activated receptor-2 (PAR-2), CD40, CD40L, CD88, intracellular Ca+ elevation, and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kB). Activated microglia, astrocytes, neurons, T-cells and mast cells release these inflammatory mediators and mediate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in a vicious manner. Further, immune and inflammatory cells and inflammatory mediators from the periphery cross the defective blood-brain-barrier (BBB) and augment neuroinflammation. Though inflammation is crucial in the onset and the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, anti-inflammatory drugs do not provide significant therapeutic effects in these patients till date, as the disease pathogenesis is not yet clearly understood. In this review, we discuss the possible factors involved in neuroinflammation-mediated neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Cytokine; Neurodegeneration; Neuroinflammation; Parkinson’s disease.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
