Prophylactic Ketamine Attenuates Learned Fear
- PMID: 28128336
- PMCID: PMC5518899
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2017.19
Prophylactic Ketamine Attenuates Learned Fear
Abstract
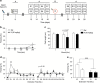
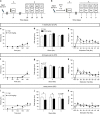
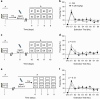
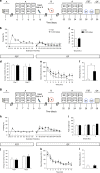
Ketamine has been reported to be an efficacious antidepressant for major depressive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder. Most recently, ketamine has also been shown to be prophylactic against stress-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. It remains unknown, however, when ketamine should be administered relative to a stressor in order to maximize its antidepressant and/or prophylactic effects. Moreover, it is unknown whether ketamine can be prophylactic against subsequent stressors. We systematically administered ketamine at different time points relative to a fear experience, in order to determine when ketamine is most effective at reducing fear expression or preventing fear reactivation. Using a contextual fear conditioning (CFC) paradigm, mice were administered a single dose of saline or ketamine (30 mg/kg) at varying time points before or after CFC. Mice administered prophylactic ketamine 1 week, but not 1 month or 1 h before CFC, exhibited reduced freezing behavior when compared with mice administered saline. In contrast, ketamine administration following CFC or during extinction did not alter subsequent fear expression. However, ketamine administered before reinstatement increased the number of rearing bouts in an open field, possibly suggesting an increase in attentiveness. These data indicate that ketamine can buffer a fear response when given a week before as prophylactic, but not when given immediately before or after a stress-inducing episode. Thus, ketamine may be most useful in the clinic if administered in a prophylactic manner 1 week before a stressor, in order to protect against heightened fear responses to aversive stimuli.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ventral CA3 Activation Mediates Prophylactic Ketamine Efficacy Against Stress-Induced Depressive-like Behavior.Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Dec 1;84(11):846-856. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.02.011. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29615190 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic (R,S)-Ketamine Is Effective Against Stress-Induced Behaviors in Adolescent but Not Aged Mice.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022 Jun 21;25(6):512-523. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyac020. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35229871 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic (R,S)-ketamine selectively protects against inflammatory stressors.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jan 27;378:112238. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112238. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31563463
-
Ketamine as a prophylactic resilience-enhancing agent.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 28;13:833259. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.833259. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35966469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Ketamine on Rodent Fear Memory.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 28;21(19):7173. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197173. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32998470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Ketamine Facilitates Fear Memory Extinction in a Rat Model of PTSD Along With Restoring Glutamatergic Alterations and Dendritic Atrophy in the Prefrontal Cortex.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 17;13:759626. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.759626. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370690 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptors in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 27;25(7):3733. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073733. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurobiological Mechanisms of Stress Resilience and Implications for the Aged Population.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018 Mar 5;16(3):234-270. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170818095105. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28820053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluoroethylnormemantine, A Novel Derivative of Memantine, Facilitates Extinction Learning Without Sensorimotor Deficits.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Jul 14;24(6):519-531. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyab007. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33631001 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine differentially affects implicit and explicit memory processes in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Jun;242(6):1245-1258. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06720-8. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 39589435
References
-
- Ardalan M, Wegener G, Polsinelli B, Madsen TM, Nyengaard JR (2016. a). Neurovascular plasticity of the hippocampus one week after a single dose of ketamine in genetic rat model of depression. Hippocampus 26: 1414–1423. - PubMed
-
- Argolo FC, Cavalcanti-Ribeiro P, Netto LR, Quarantini LC (2015). Prevention of posttraumatic stress disorder with propranolol: a meta-analytic review. J Psychosom Res 79: 89–93. - PubMed
-
- Bailey KR, Crawley JN. Anxiety-related behaviors in mice. In: Buccafusco, JJ (ed.). Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience, Chapter 5: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009 (Boca Raton, FL).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

