Vitamin E for Alzheimer's dementia and mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 28128435
- PMCID: PMC6464807
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub4
Vitamin E for Alzheimer's dementia and mild cognitive impairment
Update in
-
Vitamin E for Alzheimer's dementia and mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28418065 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Vitamin E occurs naturally in the diet. It has several biological activities, including functioning as an antioxidant to scavenge toxic free radicals. Evidence that free radicals may contribute to the pathological processes behind cognitive impairment has led to interest in the use of vitamin E supplements to treat mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). This is an update of a Cochrane Review first published in 2000, and previously updated in 2006 and 2012.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy of vitamin E in the treatment of MCI and dementia due to AD.
Search methods: We searched the Specialized Register of the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group (ALOIS), the Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, CINAHL, LILACS as well as many trials databases and grey literature sources on 22 April 2016 using the terms: "Vitamin E", vitamin-E, alpha-tocopherol.
Selection criteria: We included all double-blind, randomised trials in which treatment with any dose of vitamin E was compared with placebo in people with AD or MCI.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We rated the quality of the evidence using the GRADE approach. Where appropriate we attempted to contact authors to obtain missing information.
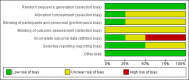
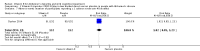
Main results: Four trials met the inclusion criteria, but we could only extract outcome data in accordance with our protocol from two trials, one in an AD population (n = 304) and one in an MCI population (n = 516). Both trials had an overall low to unclear risk of bias. It was not possible to pool data across studies owing to a lack of comparable outcome measures.In people with AD, we found no evidence of any clinically important effect of vitamin E on cognition, measured with change from baseline in the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale - Cognitive subscale (ADAS-Cog) over six to 48 months (mean difference (MD) -1.81, 95% confidence interval (CI) -3.75 to 0.13, P = 0.07, 1 study, n = 272; moderate quality evidence). There was no evidence of a difference between vitamin E and placebo groups in the risk of experiencing at least one serious adverse event over six to 48 months (risk ratio (RR) 0.86, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.05, P = 0.13, 1 study, n = 304; moderate quality evidence), or in the risk of death (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.52 to 1.34, P = 0.46, 1 study, n = 304; moderate quality evidence). People with AD receiving vitamin E showed less functional decline on the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study/Activities of Daily Living Inventory than people receiving placebo at six to 48 months (mean difference (MD) 3.15, 95% CI 0.07 to 6.23, P = 0.04, 1 study, n = 280; moderate quality evidence). There was no evidence of any clinically important effect on neuropsychiatric symptoms measured with the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (MD -1.47, 95% CI -4.26 to 1.32, P = 0.30, 1 study, n = 280; moderate quality evidence).We found no evidence that vitamin E affected the probability of progression from MCI to probable dementia due to AD over 36 months (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.35, P = 0.81, 1 study, n = 516; moderate quality evidence). Five deaths occurred in each of the vitamin E and placebo groups over the 36 months (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.30 to 3.44, P = 0.99, 1 study, n = 516; moderate quality evidence). We were unable to extract data in accordance with the review protocol for other outcomes. However, the study authors found no evidence that vitamin E differed from placebo in its effect on cognitive function, global severity or activities of daily living . There was also no evidence of a difference between groups in the more commonly reported adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: We found no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD. However, there is moderate quality evidence from a single study that it may slow functional decline in AD. Vitamin E was not associated with an increased risk of serious adverse events or mortality in the trials in this review. These conclusions have changed since the previous update, however they are still based on small numbers of trials and participants and further research is quite likely to affect the results.
Conflict of interest statement
Nicolas Farina ‐ None known David Llewellyn ‐ None known Mokhtar Gad El Kareem Nasr Isaac‐ None known Naji Tabet ‐ None known
Figures









Update of
-
Vitamin E for Alzheimer's dementia and mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11(11):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 27;1:CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub4. PMID: 23152215 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
-
- Dysken MW, Guarino PD, Vertrees JE, Asthana S, Sano M, Llorente M, et al. Vitamin E and memantine in Alzheimer's disease: clinical trial methods and baseline data. Alzheimer's & Dementia: the Journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2014;10(1):36‐44. [] - PMC - PubMed
- Dysken MW, Sano M, Asthana S, Vertrees JE, Pallaki M, Llorente M, et al. Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer. JAMA 2014;311(11):1161. [] - PMC - PubMed
- Dysken MW, Sano M, Asthana S, Vertrees JE, Pallaki M, Llorente M, et al. Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer disease: the TEAM‐AD VA cooperative randomized trial. JAMA 2014;311(1):33‐44. [] - PMC - PubMed
-
3262292
-
- Lloret A, Badía MC, Mora NJ, Pallardó FV, Alonso MD, Viña J. Vitamin E paradox in Alzheimer's disease: it does not prevent loss of cognition and may even be detrimental. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2009;17(1):143‐9. [] - PubMed
-
3262296
-
- Petersen R, Grundman R, Thomas R, Thal L. Donepezil and vitamin E as treatments for mild cognitive impairment. NeuroBiology of Aging 2004;25(S2):20. []
- Petersen RC, Thomas RG, Grundman M, Bennett D, Doody R, Ferris S, et al. for the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study Group. Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;352(23):2379‐88. [] - PubMed
-
3262298
-
- Sano M, Ernesto C, Klauber MR, Schafer K, Woodbury P, Thomas R, et al. and members of the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study. Rationale and design of a multicenter study of selegiline and a‐tocopherol in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease using novel clinical outcomes. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1996;10(3):132‐40. [] - PubMed
- Sano M, Ernesto C, Thomas RG, Klauber MR, Schafer K, Grundman M, et al. Effects of selegiline and alpha‐tocopherol on cognitive and functional outcome measures in moderately impaired patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1997;48(3):A377‐8. []
- Sano M, Ernesto C, Thomas RG, Klauber MR, Schafer K, Grundman M, et al. for the members of the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study. A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha‐tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer's disease. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;336(17):1216‐22. [] - PubMed
- Sano M, Growdon J, Klauber M, Ernesto C, Schafer P, Woodbury P, et al. Expanding the severity range of patients in clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease: a multicentre clinical trial of selegiline and a‐tocopherol. Neurology 1996;45 Suppl 4:289. []
-
3262301
References to studies excluded from this review
-
- Alavi Naeini AM, Elmadfa I, Djazayeri A, Barekatain M, Aghayeghazvini MR, Jalali M, et al. Effect of vitamin E and C supplementation on elderly with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in Isfahan, Iran. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism 2013:1145. []
-
3262306
-
- Alavi Naeini AM, Elmadfa I, Djazayery A, Barekatain M, Aghaye Ghazvini MR, Djalali M, et al. The effect of antioxidant vitamins E and C on cognitive performance of the elderly with mild cognitive impairment in Isfahan, Iran: a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. European Journal of Nutrition 2014;53(5):1255‐62. [] - PubMed
-
3262308
-
- Alzoubi KH, Khabour OF, Abu Rashid B, Damaj IM, Salah HA. The neuroprotective effect of vitamin E on chronic sleep deprivation‐induced memory impairment: the role of oxidative stress. Behavioural Brain Research 2012;226(1):205‐10. [] - PubMed
-
3262310
-
- Anand VPR, Kumar BJ, Varghese JM, Das SK. Supplementation of vitamin E improves cognitive status and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus. International Research Journal of Pharmacy 2011;2(11):169‐72. []
-
3262312
-
- Anonymous. High dose vitamin E may slow Alzheimer's decline. Harvard Men's Health Watch 2014;18(8):8. [] - PubMed
-
3262316
References to ongoing studies
-
- Gopal V. A pilot study of effect of vitamin E on cognition and measures of activities of daily living in patients with moderately severe Alzheimer's disease. National Research Register2005. []
-
3262461
Additional references
-
- Ahlskog JE, Uitti RJ, Low PA, Tyce GM, Nickander KK, Petersen RC, et al. No evidence for systemic oxidant stress in Parkinson's or Alzheimer's disease. Movement Disorders 1995;10:566‐73. - PubMed
-
- Aisen PS, Schafer KA, Grundman M, Pfeiffer E, Sano M, Davis KL, et al. the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study. Effects of rofecoxib or naproxen vs placebo on Alzheimer disease progression: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003;289(21):2819‐26. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Press, 1994.
-
- Behl C, Davis J, Cole GM, Schubert D. Vitamin E protects nerve cells from amyloid‐beta protein toxicity. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communication 1992;186:944‐50. - PubMed
-
- Berg L. Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR). Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1988;24:637‐9. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

