Single-Molecule Investigations on Histone H2A-H2B Dynamics in the Nucleosome
- PMID: 28128545
- PMCID: PMC5436051
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b01252
Single-Molecule Investigations on Histone H2A-H2B Dynamics in the Nucleosome
Abstract
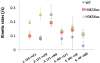
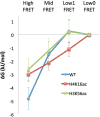
Nucleosomes impose physical barriers to DNA-templated processes, playing important roles in eukaryotic gene regulation. DNA is packaged into nucleosomes by histone proteins mainly through strong electrostatic interactions that can be modulated by various post-translational histone modifications. Investigating the dynamics of histone dissociation from the nucleosome and how it is altered upon histone modifications is important for understanding eukaryotic gene regulation mechanisms. In particular, histone H2A-H2B dimer displacement in the nucleosome is one of the most important and earliest steps of histone dissociation. Two conflicting hypotheses on the requirement for dimer displacement are that nucleosomal DNA needs to be unwrapped before a dimer can displace and that a dimer can displace without DNA unwrapping. In order to test the hypotheses, we employed three-color single-molecule FRET and monitored in a time-resolved manner the early kinetics of H2A-H2B dimer dissociation triggered by high salt concentration and by histone chaperone Nap1. The results reveal that dimer displacement requires DNA unwrapping in the vast majority of the nucleosomes in the salt-induced case, while dimer displacement precedes DNA unwrapping in >60% of the nucleosomes in the Nap1-mediated case. We also found that acetylation at histone H4K16 or H3K56 affects the kinetics of Nap1-mediated dimer dissociation and facilitates the process both kinetically and thermodynamically. On the basis of these results, we suggest a mechanism by which histone chaperone facilitates H2A-H2B dimer displacement from the histone core without requiring another factor to unwrap the nucleosomal DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
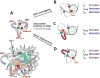


References
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Yager TD, McMurray CT, van Holde KE. Salt-induced release of DNA from nucleosome core particles. Biochemistry. 1989;28:2271–2281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

