Therapeutic miR-21 Silencing Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease in Mice
- PMID: 28129112
- PMCID: PMC5363308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.08.001
Therapeutic miR-21 Silencing Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease in Mice
Abstract
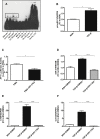
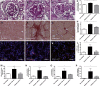
Diabetic nephropathy is the main cause of end-stage renal disease. MicroRNAs are powerful regulators of the genome, and global expression profiling revealed miR-21 to be among the most highly regulated microRNAs in kidneys of mice with diabetic nephropathy. In kidney biopsies of diabetic patients, miR-21 correlated with tubulointerstitial injury. In situ PCR analysis showed a specific enrichment of miR-21 in glomerular cells. We identified cell division cycle 25a (Cdc25a) and cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (Cdk6) as novel miR-21 targets in mesangial cells. miR-21-mediated repression of Cdc25a and Cdk6 resulted in impaired cell cycle progression and subsequent mesangial cell hypertrophy. miR-21 increased podocyte motility by regulating phosphatase and tensin homolog (Pten). miR-21 antagonism in vitro and in vivo in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice decreased mesangial expansion, interstitial fibrosis, macrophage infiltration, podocyte loss, albuminuria, and fibrotic- and inflammatory gene expression. In conclusion, miR-21 antagonism rescued various functional and structural parameters in mice with diabetic nephropathy and, thus, might be a viable option in the treatment of patients with diabetic kidney disease.
Keywords: TGF-β; cell-cycle regulators; diabetic nephropathy; mesangial hypertrophy; miR-21; microRNA; podocyte motility.
Copyright © 2017 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Raptis A.E., Viberti G. Pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. 2001;109(Suppl 2):S424–S437. - PubMed
-
- Fineberg D., Jandeleit-Dahm K.A., Cooper M.E. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013;9:713–723. - PubMed
-
- Sarnak M.J., Levey A.S., Schoolwerth A.C., Coresh J., Culleton B., Hamm L.L., McCullough P.A., Kasiske B.L., Kelepouris E., Klag M.J., American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2003;108:2154–2169. - PubMed
-
- Lorenzen J.M., Haller H., Thum T. MicroRNAs as mediators and therapeutic targets in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011;7:286–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

