Serum Metabolomics of Burkitt Lymphoma Mouse Models
- PMID: 28129369
- PMCID: PMC5271368
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170896
Serum Metabolomics of Burkitt Lymphoma Mouse Models
Abstract
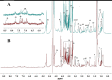
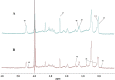
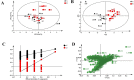
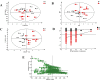
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a rare and highly aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The mortality rate of BL patients is very high due to the rapid growth rate and frequent systemic spread of the disease. A better understanding of the pathogenesis, more sensitive diagnostic tools and effective treatment methods for BL are essential. Metabolomics, an important aspect of systems biology, allows the comprehensive analysis of global, dynamic and endogenous biological metabolites based on their nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS). It has already been used to investigate the pathogenesis and discover new biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis. In this study, we analyzed differences of serum metabolites in BL mice and normal mice by NMR-based metabolomics. We found that metabolites associated with energy metabolism, amino acid metabolism, fatty acid metabolism and choline phospholipid metabolism were altered in BL mice. The diagnostic potential of the metabolite differences was investigated in this study. Glutamate, glycerol and choline had a high diagnostic accuracy; in contrast, isoleucine, leucine, pyruvate, lysine, α-ketoglutarate, betaine, glycine, creatine, serine, lactate, tyrosine, phenylalanine, histidine and formate enabled the accurate differentiation of BL mice from normal mice. The discovery of abnormal metabolism and relevant differential metabolites may provide useful clues for developing novel, noninvasive approaches for the diagnosis and prognosis of BL based on these potential biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
JD is employed by a commercial company, JOINN Laboratories, Inc., Beijing, China. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This affiliation does not alter PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma metabolites in childhood Burkitt lymphoma cases and cancer-free controls in Uganda.Metabolomics. 2024 Jun 28;20(4):67. doi: 10.1007/s11306-024-02130-1. Metabolomics. 2024. PMID: 38940866 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic signatures of esophageal cancer: NMR-based metabolomics and UHPLC-based focused metabolomics of blood serum.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1832(8):1207-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.03.009. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23524237
-
Comprehensive Metaboproteomics of Burkitt's and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Lines and Primary Tumor Tissues Reveals Distinct Differences in Pyruvate Content and Metabolism.J Proteome Res. 2017 Mar 3;16(3):1105-1120. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00164. Epub 2017 Feb 16. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 28161958
-
Risk factors for the evaluation of potential central nervous system metastasis in Burkitt's lymphoma: a case study and literature review.Hematol Oncol. 2016 Mar;34(1):36-41. doi: 10.1002/hon.2159. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 25312095 Review.
-
Burkitt lymphoma versus diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a practical approach.Hematol Oncol. 2009 Dec;27(4):182-5. doi: 10.1002/hon.914. Hematol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19670467 Review.
Cited by
-
A metabolomic study on early detection of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 10;9(8):7984-7995. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24150. eCollection 2018 Jan 30. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29487708 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism in B cell biology.Mol Oncol. 2024 Jul;18(7):1795-1813. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13560. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38013654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMR-based metabolomic profiling can differentiate follicular lymphoma from benign lymph node tissues and may be predictive of outcome.Sci Rep. 2022 May 18;12(1):8294. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12445-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35585165 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Burkitt lymphoma with a tumor cell-specific heptamethine carbocyanine-cisplatin conjugate.Cancer. 2019 Jul 1;125(13):2222-2232. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32033. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30840322 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of 10 lymphoma datasets identifies E2F8 as a key regulator in Burkitt's lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Jul 15;11(7):4382-4396. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31396343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burkitt D. A Sarcoma Involving the Jaws in African Children. Brit J Surg. 1958; 46: 218–223. - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JKC, Cleary ML, et al. A Revised European-American Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms—a Proposal from the International Lymphoma Study-Group. Blood. 1994; 84: 1361–1392. - PubMed
-
- Braziel RM, Arber DA, Slovak ML, Gulley ML, Spier C, Kjeldsberg C, et al. The Burkitt-like lymphomas: a Southwest Oncology Group study delineating phenotypic, genotypic, and clinical features. Blood. 2001; 97: 3713–3720. - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J, et al. World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: Report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting—Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17: 3835–3849. 10.1200/jco.1999.17.12.3835 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

