Cellular and Circuit Mechanisms Shaping the Perceptual Properties of the Primate Fovea
- PMID: 28129540
- PMCID: PMC5298833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.005
Cellular and Circuit Mechanisms Shaping the Perceptual Properties of the Primate Fovea
Abstract
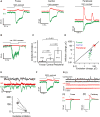
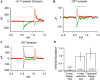
The fovea is a specialized region of the retina that dominates the visual perception of primates by providing high chromatic and spatial acuity. While the foveal and peripheral retina share a similar core circuit architecture, they exhibit profound functional differences whose mechanisms are unknown. Using intracellular recordings and structure-function analyses, we examined the cellular and synaptic underpinnings of the primate fovea. Compared to peripheral vision, the fovea displays decreased sensitivity to rapid variations in light inputs; this difference is reflected in the responses of ganglion cells, the output cells of the retina. Surprisingly, and unlike in the periphery, synaptic inhibition minimally shaped the responses of foveal midget ganglion cells. This difference in inhibition cannot however, explain the differences in the temporal sensitivity of foveal and peripheral midget ganglion cells. Instead, foveal cone photoreceptors themselves exhibited slower light responses than peripheral cones, unexpectedly linking cone signals to perceptual sensitivity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Vision: Two Speeds in the Retina.Curr Biol. 2017 Apr 24;27(8):R303-R305. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.02.056. Curr Biol. 2017. PMID: 28441563
References
-
- Abbott CJ, Percival KA, Martin PR, Grünert U. Amacrine and bipolar inputs to midget and parasol ganglion cells in marmoset retina. Vis Neurosci. 2012;29:157–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

