Effects of mindfulness, reappraisal, and suppression on sad mood and cognitive resources
- PMID: 28129574
- PMCID: PMC5509409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brat.2017.01.006
Effects of mindfulness, reappraisal, and suppression on sad mood and cognitive resources
Abstract
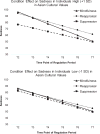
The present study investigated the relative effects of mindfulness, reappraisal and suppression in reducing sadness, and the extent to which implementation of these strategies affects cognitive resources in a laboratory context. A total of 171 Singaporean undergraduate participants were randomly assigned to receive brief training in mindfulness, reappraisal, or suppression prior to undergoing a sad mood induction. Individual adherence to Asian cultural values was assessed as a potential moderator of strategy effectiveness. Participants rated their mood and completed a Color-Word Stroop task before and after mood regulation instructions. Analyses using multi-level modelling showed that the suppression condition caused less robust declines in sadness over time compared to mindfulness. There was also a nonsignificant trend in which mindfulness was associated with greater sadness recovery compared to reappraisal. Suppression resulted in lower average sadness compared to mindfulness among those high on Asian cultural values, but not those low on Asian cultural values. Both mindfulness and reappraisal buffered against increases in Stroop interference from pre-to post-regulation compared to suppression. The findings highlight the advantage of mindfulness as a strategy effective not only in the regulation of sad mood, but also in the preservation of cognitive resources in the context of mood regulation.
Keywords: Asian cultural values; Cognitive resources; Mindfulness; Reappraisal; Sad mood; Suppression.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Alberts H, Schneider F, Martjin C. Dealing efficiently with emotions: Acceptance-based coping with negative emotions require fewer resources than suppression. Cognition & Emotion. 2012;26:863–870. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2011.625402. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aldao A, Nolen-Hoeksema S, Schweizer S. Emotion-regulation strategies across psychopathology: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review. 2010;30:217–237. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2009.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arch JJ, Craske MG. Mechanisms of mindfulness: Emotion regulation following a focused breathing induction. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2006;44:1849–1858. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2005.12.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braams BR, Blechert J, Boden TM, Gross JJ. The effects of acceptance and suppression on anticipation and receipt of pain stimulation. Behaviour Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry. 2012;43:1014–1018. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2012.04.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Broderick PC. Mindfulness and coping with dysphoric mood: Contrasts with rumination and distraction. Cognitive Therapy and Research. 2005;29(5):501–510.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

