Tissue engineering the mechanosensory circuit of the stretch reflex arc with human stem cells: Sensory neuron innervation of intrafusal muscle fibers
- PMID: 28129596
- PMCID: PMC5299592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.005
Tissue engineering the mechanosensory circuit of the stretch reflex arc with human stem cells: Sensory neuron innervation of intrafusal muscle fibers
Abstract
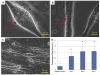
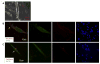
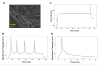
Muscle spindles are sensory organs embedded in the belly of skeletal muscles that serve as mechanoreceptors detecting static and dynamic information about muscle length and stretch. Through their connection with proprioceptive sensory neurons, sensation of axial body position and muscle movement are transmitted to the central nervous system. Impairment of this sensory circuit causes motor deficits and has been linked to a wide range of diseases. To date, no defined human-based in vitro model of the proprioceptive sensory circuit has been developed. The goal of this study was to develop a human-based in vitro muscle sensory circuit utilizing human stem cells. A serum-free medium was developed to drive the induction of intrafusal fibers from human satellite cells by actuation of a neuregulin signaling pathway. Both bag and chain intrafusal fibers were generated and subsequently validated by phase microscopy and immunocytochemistry. When co-cultured with proprioceptive sensory neurons derived from human neuroprogenitors, mechanosensory nerve terminal structural features with intrafusal fibers were demonstrated. Most importantly, patch-clamp electrophysiological analysis of the intrafusal fibers indicated repetitive firing of human intrafusal fibers, which has not been observed in human extrafusal fibers.
Keywords: Human; Intrafusal fiber; In vitro; Proprietary sensory circuit; Serum-free medium; Stem cells.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Maier A. Development and regeneration of muscle spindles in mammals and birds. Int J Dev Biol. 1997;41:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Chen HH, Hippenmeyer S, Arber S, Frank E. Development of the mono-synaptic stretch reflex circuit. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:96–102. - PubMed
-
- Liu JX, Eriksson PO, Thornell LE, Pedrosa-Domellöf F. Myosin heavy chain composition of muscle spindles in human biceps brachii. J Histochem Cytochem. 2002;50:171–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

