The dynamics of disease in a metapopulation: The role of dispersal range
- PMID: 28130098
- PMCID: PMC5360276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.01.037
The dynamics of disease in a metapopulation: The role of dispersal range
Abstract
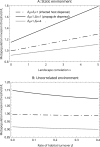
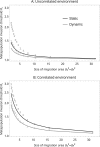
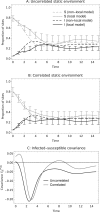
The establishment and spread of a disease within a metapopulation is influenced both by dynamics within each population and by the host and pathogen spatial processes through which they are connected. We develop a spatially explicit metapopulation model to investigate how the form of host and disease dispersal jointly influence the probability of disease establishment and invasion. We show that diseases are more likely to establish if both the host and the disease tend to disperse locally, since the former leads to the spatial aggregation of host populations in the environment while the latter facilitates the pathogen's exploitation of this spatial pattern. In contrast, local pathogen dispersal is likely to reduce the probability of subsequent disease spread because it increases the spatial segregation of infected and uninfected populations. The effects of local dispersal on disease dynamics are less pronounced when the pathogen spreads through the movement of infected hosts and more pronounced when pathogen dispersal is independent (for example through airborne viruses) though the details of host and pathogen biology can be important. These spatial effects tend to be more pronounced if the sites available for host occupation are themselves spatially aggregated.
Keywords: Correlated landscape; Disease; Dispersal kernel; Metapopulation; Spatial moments.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Ball F., Mollison D., Scalia-Tomba G. Epidemics with two levels of mixing. Ann. Appl. Probab. 1997;7:46–89.
-
- Bolker B. Combining endogenous and exogenous spatial variability in analytical population models. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2003;64(3):255–270. - PubMed
-
- Bolker B., Pacala S.W. Using moment equations to understand stochastically driven spatial pattern formation in ecological systems. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1997;52(3):179–197. - PubMed
-
- Bolker B.M. Analytic models for the patchy spread of plant disease. Bull. Math. Biol. 1999;61(5):849–874. - PubMed
-
- Brown D.H., Bolker B.M. The effects of disease dispersal and host clustering on the epidemic threshold in plants. Bull. Math. Biol. 2004;66(2):341–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

