Interleukin-1 signaling in the basolateral amygdala is necessary for heroin-conditioned immunosuppression
- PMID: 28131792
- PMCID: PMC5828772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.01.017
Interleukin-1 signaling in the basolateral amygdala is necessary for heroin-conditioned immunosuppression
Abstract
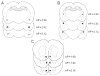
Heroin administration suppresses the production of inducible nitric oxide (NO), as indicated by changes in splenic inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and plasma nitrate/nitrite. Since NO is a measure of host defense against infection and disease, this provides evidence that heroin can increase susceptibility to pathogens by directly interacting with the immune system. Previous research in our laboratory has demonstrated that these immunosuppressive effects of heroin can also be conditioned to environmental stimuli by repeatedly pairing heroin administration with a unique environmental context. Re-exposure to a previously drug-paired context elicits immunosuppressive effects similar to heroin administration alone. In addition, our laboratory has reported that the basolateral amygdala (BLA) and medial nucleus accumbens shell (mNAcS) are critical neural substrates that mediate this conditioned effect. However, our understanding of the contributing mechanisms within these brain regions is limited. It is known that the cytokine interleukin-1 (IL-1) plays an important role in learning and memory. In fact, our laboratory has demonstrated that inhibition of IL-1β expression in the dorsal hippocampus (DH) prior to re-exposure to a heroin-paired context prevents the suppression of measures of NO production. Therefore, the present studies sought to further investigate the role of IL-1 in heroin-conditioned immunosuppression. Blockade of IL-1 signaling in the BLA, but not in the caudate putamen or mNAcS, using IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) attenuated heroin-conditioned immunosuppression of NO production as measured by plasma nitrate/nitrite and iNOS mRNA expression in spleen tissue. Taken together, these findings suggest that IL-1 signaling in the BLA is necessary for the expression of heroin-conditioned immunosuppression of NO production and may be a target for interventions that normalize immune function in heroin users and patient populations exposed to opiate regimens.
Keywords: Basolateral amygdala; Heroin; IL-1; IL-1 receptor antagonist; Immune conditioning, opioid; Learning; Nitric oxide.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
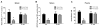
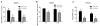
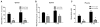
Similar articles
-
Acquisition of heroin conditioned immunosuppression requires IL-1 signaling in the dorsal hippocampus.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Aug;56:325-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 27072068 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned effects of heroin on proinflammatory mediators require the basolateral amygdala.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Nov;28(9):1867-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06472.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18973600 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal hippocampal neural immune signaling regulates heroin-conditioned immunomodulation but not heroin-conditioned place preference.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Oct;73:698-707. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.07.024. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 30075289 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the basolateral amygdala and infralimbic cortex in (re)learning extinction.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):303-312. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4957-x. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 29959461 Review.
-
Basolateral amygdala, nicotinic cholinergic receptors, and nicotine: Pharmacological effects and addiction in animal models and humans.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Aug;50(3):2247-2254. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13970. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 29802666 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals with opioid use disorder with brain organoids.J Tissue Eng. 2021 Feb 26;12:2041731420985299. doi: 10.1177/2041731420985299. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2021. PMID: 33738089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conditioning the neuroimmune response to ethanol using taste and environmental cues in adolescent and adult rats.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019 Apr;244(5):362-371. doi: 10.1177/1535370219831709. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019. PMID: 30808184 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the reciprocal interactions between neuroinflammatory processes and substance use and misuse, with a focus on alcohol misuse.Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2023 May 4;49(3):269-282. doi: 10.1080/00952990.2023.2201944. Epub 2023 May 6. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2023. PMID: 37148274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Type-Specific Interleukin 1 Receptor 1 Signaling in the Brain Regulates Distinct Neuroimmune Activities.Immunity. 2019 Feb 19;50(2):317-333.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.012. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 30683620 Free PMC article.
-
CCR5 mediates HIV-1 Tat-induced neuroinflammation and influences morphine tolerance, dependence, and reward.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Mar;69:124-138. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 29146238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avital A, Goshen I, Kamsler A, Segal M, Iverfeldt K, Richter-Levin G, Yirmiya R. Impaired interleukin-1 signaling is associated with deficits in hippocampal memory processes and neural plasticity. Hippocampus. 2003;13:826– 834. - PubMed
-
- Beattie EC, Stellwagen D, Morishita W, Bresnahan JC, Ha BK, Von Zastrow M, Beattie MS, Malenka RC. Control of synaptic strength by glial TNFalpha. Science. 2002;295:2282–2285. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

