Growing challenges for HIV programmes in Asia: clinic population trends, 2003-2013
- PMID: 28132544
- PMCID: PMC5534184
- DOI: 10.1080/09540121.2017.1282108
Growing challenges for HIV programmes in Asia: clinic population trends, 2003-2013
Abstract
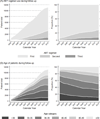
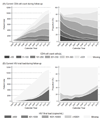
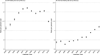
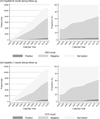
The scale-up of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has led to a substantial change in the clinical population of HIV-positive patients receiving care. We describe the temporal trends in the demographic and clinical characteristics of HIV-positive patients initiating ART in 2003-13 within an Asian regional cohort. All HIV-positive adult patients that initiated ART between 2003 and 2013 were included. We summarized ART regimen use, age, CD4 cell count, HIV viral load, and HIV-related laboratory monitoring rates during follow-up by calendar year. A total of 16 962 patients were included in the analysis. Patients in active follow-up increased from 695 patients at four sites in 2003 to 11,137 patients at eight sites in 2013. The proportion of patients receiving their second or third ART regimen increased over time (5% in 2003 to 29% in 2013) along with patients aged ≥50 years (8% in 2003 to 18% in 2013). Concurrently, CD4 monitoring has remained stable in recent years, whereas HIV viral load monitoring, although varied among the sites, is increasing. There have been substantial changes in the clinical and demographic characteristics of HIV-positive patients receiving ART in Asia. HIV programmes will need to anticipate the clinical care needs for their aging populations, expanded viral load monitoring, and, the eventual increase in second and third ART regimens that will lead to higher costs and more complex drug procurement needs.
Keywords: ART; Asia; HIV; characteristics; clinical; demographics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved survival in HIV treatment programmes in Asia.Antivir Ther. 2016;21(6):517-527. doi: 10.3851/IMP3041. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Antivir Ther. 2016. PMID: 26961354 Free PMC article.
-
Improved virologic outcomes over time for HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy in a cohort from Rio de Janeiro, 1997-2011.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Jun 11;14:322. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-322. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24919778 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Trends in CD4 cell count response to first-line antiretroviral treatment in HIV-positive patients from Asia, 2003-2013: TREAT Asia HIV Observational Database Low Intensity Transfer.Int J STD AIDS. 2017 Nov;28(13):1282-1291. doi: 10.1177/0956462417699538. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Int J STD AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28632481 Free PMC article.
-
[Consensus document of Gesida and Spanish Secretariat for the National Plan on AIDS (SPNS) regarding combined antiretroviral treatment in adults infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (January 2012)].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2012 Jun;30(6):e1-89. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2012.03.006. Epub 2012 May 23. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2012. PMID: 22633764 Spanish.
-
[Recommendations from the GESIDA/Spanish AIDS Plan regarding antiretroviral treatment in adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection (update February 2009)].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009 Apr;27(4):222-35. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2008.11.002. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009. PMID: 19246124 Spanish.
Cited by
-
Antiretroviral Long-Term Efficacy and Resistance of Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Lamivudine in HIV-1-Infected Treatment-Naïve Patients (ALTERLL): 144-Week Results of a Randomized, Open-Label, Non-Inferiority Study From Guangdong, China.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;11:569766. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.569766. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33841131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ball SC. The aging HIV population. Clinical Practice. 2014;11(2):221–231.
-
- Bonner K, Mezochow A, Roberts T, Ford N, Cohn J. Viral Load Monitoring as a Tool to Reinforce Adherence: A Systematic Review. Jaids-Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2013;64(1):74–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
