Non-Canonical and Sexually Dimorphic X Dosage Compensation States in the Mouse and Human Germline
- PMID: 28132849
- PMCID: PMC5300051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.12.023
Non-Canonical and Sexually Dimorphic X Dosage Compensation States in the Mouse and Human Germline
Abstract
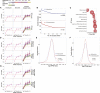
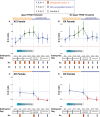
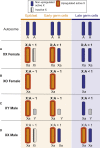
Somatic X dosage compensation requires two mechanisms: X inactivation balances X gene output between males (XY) and females (XX), while X upregulation, hypothesized by Ohno and documented in vivo, balances X gene with autosomal gene output. Whether X dosage compensation occurs in germ cells is unclear. We show that mouse and human germ cells exhibit non-canonical X dosage states that differ from the soma and between the sexes. Prior to genome-wide reprogramming, X upregulation is present, consistent with Ohno's hypothesis. Subsequently, however, it is erased. In females, erasure follows loss of X inactivation, causing X dosage excess. Conversely, in males, erasure leads to permanent X dosage decompensation. Sex chromosomally abnormal models exhibit a "sex-reversed" X dosage state: XX males, like XX females, develop X dosage excess, while XO females, like XY males, develop X dosage decompensation. Thus, germline X dosage compensation states are determined by X chromosome number, not phenotypic sex. These unexpected differences in X dosage compensation states between germline and soma offer unique perspectives on sex chromosome infertility.
Keywords: X inactivation; X upregulation; dosage compensation; genome-wide reprogramming; germline development; sex chromosomes.
Copyright © 2017 The Francis Crick Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mammalian X Chromosome Dosage Compensation: Perspectives From the Germ Line.Bioessays. 2018 Jun;40(6):e1800024. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800024. Epub 2018 May 14. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 29756331 Review.
-
Dosage Compensation of the X Chromosomes in Bovine Germline, Early Embryos, and Somatic Tissues.Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Jan 1;11(1):242-252. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy270. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 30566637 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Dosage Compensation in Anolis carolinensis, a Reptile with XX/XY Chromosomal Sex Determination.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 Jan 1;9(1):231-240. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw263. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28206607 Free PMC article.
-
No X-chromosome dosage compensation in human proteomes.Mol Biol Evol. 2015 Jun;32(6):1456-60. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv036. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Mol Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25697342 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of X-chromosome dosage compensation in human: mechanisms and model systems.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;372(1733):20160363. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0363. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28947660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of gene dosage on the Z-chromosome of schistosome parasites.Elife. 2018 Jul 25;7:e35684. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35684. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30044216 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional progression during meiotic prophase I reveals sex-specific features and X chromosome dynamics in human fetal female germline.PLoS Genet. 2021 Sep 9;17(9):e1009773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009773. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34499650 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually dimorphic DNA damage responses and mutation avoidance in the mouse germline.Genes Dev. 2020 Dec 1;34(23-24):1637-1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.341602.120. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 33184219 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian primordial germ cell specification.Development. 2021 Mar 15;148(6):dev189217. doi: 10.1242/dev.189217. Development. 2021. PMID: 33722957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NSD1-deposited H3K36me2 directs de novo methylation in the mouse male germline and counteracts Polycomb-associated silencing.Nat Genet. 2020 Oct;52(10):1088-1098. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0689-z. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Nat Genet. 2020. PMID: 32929285
References
-
- Adler D.A., Rugarli E.I., Lingenfelter P.A., Tsuchiya K., Poslinski D., Liggitt H.D., Chapman V.M., Elliott R.W., Ballabio A., Disteche C.M. Evidence of evolutionary up-regulation of the single active X chromosome in mammals based on Clc4 expression levels in Mus spretus and Mus musculus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997;94:9244–9248. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birchler J.A. Claims and counterclaims of X-chromosome compensation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012;19:3–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

