Informatics-based Challenges of Building Collaborative Healthcare Research and Analysis Networks from Rural Community Health Centers
- PMID: 28133639
- PMCID: PMC5264517
- DOI: 10.1109/BHI.2016.7455947
Informatics-based Challenges of Building Collaborative Healthcare Research and Analysis Networks from Rural Community Health Centers
Abstract
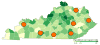
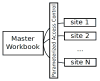
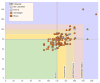
We discuss informatics-based challenges of constructing large-scale collaborative networks for healthcare research and analysis from rural community health centers. These types of networks provide data access and analytic insights across multiple heterogeneous health centers for both healthcare professionals and biomedical researchers. Challenges fall into three general categories: data access, data integration, and technical infrastructure. Data access issues arise in balancing patient privacy, security, and utility; data integration issues persist from each site independently operating its desired electronic medical record; technical infrastructure challenges include creating an analysis and reporting hub capable of scaling across a large collaborative network. Other challenges, such as the difficulty of site recruitment, are important to discuss, but cannot be solved directly through informatics alone. We discuss these challenges and their potential solutions in the context of our implementation of the Kentucky Diabetes and Obesity Collaborative (KDOC). KDOC is a network of Federally-Qualified Community Health Centers (FQHCs) that established a collaborative infrastructure for research and analysis of obesity and diabetes in rural and under-served communities.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using i2b2 to Bootstrap Rural Health Analytics and Learning Networks.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2016 Aug;2016:2533-2536. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2016.7591246. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2016. PMID: 28261006 Free PMC article.
-
Research Partnerships with Healthcare Providers in Rural Community Health Centers: Needs and Challenges in Diabetes Research.Public Health Front. 2015 Mar;4(1):1-6. doi: 10.5963/phf0401001. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Public Health Front. 2015. PMID: 26457246 Free PMC article.
-
At the crossroads: NRTRC white paper examines trends driving the convergence of telehealth, EHRs and HIE.World Hosp Health Serv. 2010;46(4):17-23. World Hosp Health Serv. 2010. PMID: 21391447
-
Pediatric collaborative networks for quality improvement and research.Acad Pediatr. 2013 Nov-Dec;13(6 Suppl):S69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2013.07.004. Acad Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 24268088 Review.
-
Building the informatics infrastructure for comparative effectiveness research (CER): a review of the literature.Med Care. 2012 Jul;50 Suppl:S38-48. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e318259becd. Med Care. 2012. PMID: 22692258 Review.
Cited by
-
Using Closure Tables to Enable Cross-Querying of Ontologies in Database-Driven Applications.IEEE EMBS Int Conf Biomed Health Inform. 2017 Feb;2017:493-496. doi: 10.1109/BHI.2017.7897313. Epub 2017 Apr 13. IEEE EMBS Int Conf Biomed Health Inform. 2017. PMID: 28725879 Free PMC article.
-
Gaps in Artificial Intelligence Research for Rural Health in the United States: A Scoping Review.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 27:2025.06.26.25330361. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.26.25330361. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40666334 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Empowering Implementation Teams with a Learning Health System Approach: Leveraging Data to Improve Quality of Care for Transient Ischemic Attack.J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Nov;35(Suppl 2):823-831. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-06160-y. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Gen Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32875510 Free PMC article.
-
Using i2b2 to Bootstrap Rural Health Analytics and Learning Networks.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2016 Aug;2016:2533-2536. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2016.7591246. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2016. PMID: 28261006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carswell P, Manning B, Long J, Braithwaite J. Building clinical networks: a developmental evaluation framework. BMJ Quality & Safety. 2014;23(5):422–427. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
