New arylsparteine derivatives as positive inotropic drugs
- PMID: 28133984
- PMCID: PMC6009970
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1279156
New arylsparteine derivatives as positive inotropic drugs
Abstract
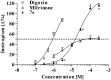
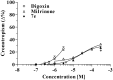
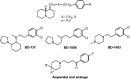
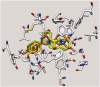
Positive inotropic agents are fundamental in the treatment of heart failure; however, their arrhythmogenic liability and the increased myocardial oxygen demand strongly limit their therapeutic utility. Pursuing our study on cardiovascular activities of lupin alkaloid derivatives, several 2-(4-substituted-phenyl)-2-dehydrosparteines and 2-(4-substituted-phenyl)sparteines were prepared and tested for inotropic and chronotropic activities on isolated guinea pig atria. Four compounds (6b, 6e, 7b, and 7f) exhibited significant inotropism that, at the higher concentrations, was followed by negative inotropism or toxicity. Compound 7e (2-(4-tolyl)sparteine) exhibited a steep dose-depending inotropic activity up to the highest concentration tested (300 µM) with an Emax of 116.5 ± 3.4% of basal force, proving less potent but much more active in comparison to the highest concentrations tested of digoxin and milrinone having Emax of 87.5 ± 3.1% and 52.2 ± 1.1%, respectively. Finally, docking studies suggested that the relevant sparteine derivatives could target the sigma-1 receptor, whose involvement in cardiac activity is well documented.
Keywords: 2-aryl-2-dehydrosparteines; 2-arylsparteines; Lupin alkaloids; positive inotropic agents.
Figures
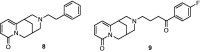
Similar articles
-
The positive inotropic and chronotropic effects of evodiamine and rutaecarpine, indoloquinazoline alkaloids isolated from the fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa, on the guinea-pig isolated right atria: possible involvement of vanilloid receptors.Planta Med. 2001 Apr;67(3):244-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-12008. Planta Med. 2001. PMID: 11345696
-
Pharmacological characterization of a new milrinone analogue.Farmaco. 1994 Jan;49(1):19-23. Farmaco. 1994. PMID: 8185745
-
Digoxin effects in the guinea pig heart: interaction with rimalkalim.Pharmacol Res. 1998 Jan;37(1):67-73. doi: 10.1006/phrs.1997.0270. Pharmacol Res. 1998. PMID: 9503482
-
A new milrinone analog: role of binding to A1 adenosine receptor in its positive inotropic effect on isolated guinea pig and rat atria.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Nov;283(2):541-7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 9353368
-
The progress towards the development of DHQO derivatives and related analogues with inotropic effects.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013 Oct;13(12):1801-11. doi: 10.2174/13895575113136660089. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24032511 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Targets and Future Directions of Positive Inotropes for Heart Failure.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(42):6971-6991. doi: 10.2174/0109298673262360231018193823. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37909442 Review.
References
-
- Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, et al. . ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). Eur Heart J 2008;29:2388–442. - PubMed
-
- Feldman AM.Classification of positive inotropic agents. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993;22:1223–7. - PubMed
-
- Francis GS, Bartos JA, Adatya S.. Inotropes. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;63:2069–78. - PubMed
-
- Endoh M, Hori M.. Basic pharmacology and clinical application of new positive inotropic agents. Drugs Today 1993;29:29–54.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
