Control of Genome Integrity by RFC Complexes; Conductors of PCNA Loading onto and Unloading from Chromatin during DNA Replication
- PMID: 28134787
- PMCID: PMC5333041
- DOI: 10.3390/genes8020052
Control of Genome Integrity by RFC Complexes; Conductors of PCNA Loading onto and Unloading from Chromatin during DNA Replication
Abstract
During cell division, genome integrity is maintained by faithful DNA replication during S phase, followed by accurate segregation in mitosis. Many DNA metabolic events linked with DNA replication are also regulated throughout the cell cycle. In eukaryotes, the DNA sliding clamp, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), acts on chromatin as a processivity factor for DNA polymerases. Since its discovery, many other PCNA binding partners have been identified that function during DNA replication, repair, recombination, chromatin remodeling, cohesion, and proteolysis in cell-cycle progression. PCNA not only recruits the proteins involved in such events, but it also actively controls their function as chromatin assembles. Therefore, control of PCNA-loading onto chromatin is fundamental for various replication-coupled reactions. PCNA is loaded onto chromatin by PCNA-loading replication factor C (RFC) complexes. Both RFC1-RFC and Ctf18-RFC fundamentally function as PCNA loaders. On the other hand, after DNA synthesis, PCNA must be removed from chromatin by Elg1-RFC. Functional defects in RFC complexes lead to chromosomal abnormalities. In this review, we summarize the structural and functional relationships among RFC complexes, and describe how the regulation of PCNA loading/unloading by RFC complexes contributes to maintaining genome integrity.
Keywords: Ctf18; DNA replication; Elg1; PCNA; PCNA loader; PCNA unloader; RFC complex; RFC1; chromatin; genome integrity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
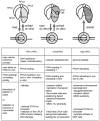
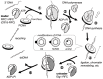

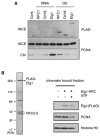
Similar articles
-
Functions of Multiple Clamp and Clamp-Loader Complexes in Eukaryotic DNA Replication.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1042:135-162. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6955-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29357057 Review.
-
Replication protein A-directed unloading of PCNA by the Ctf18 cohesion establishment complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;25(13):5445-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5445-5455.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964801 Free PMC article.
-
The Atad5 RFC-like complex is the major unloader of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in Xenopus egg extracts.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jan;300(1):105588. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105588. Epub 2023 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38141767 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM reveals a nearly complete PCNA loading process and unique features of the human alternative clamp loader CTF18-RFC.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 30;121(18):e2319727121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2319727121. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38669181 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative clamp loaders/unloaders.FEMS Yeast Res. 2016 Nov;16(7):fow084. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/fow084. Epub 2016 Sep 24. FEMS Yeast Res. 2016. PMID: 27664980 Review.
Cited by
-
Interrelationships Between miR-34a and FSH in the Control of Porcine Ovarian Cell Functions.Reprod Sci. 2023 Jun;30(6):1789-1807. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-01127-2. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36477596
-
DNA replication: Mechanisms and therapeutic interventions for diseases.MedComm (2020). 2023 Feb 5;4(1):e210. doi: 10.1002/mco2.210. eCollection 2023 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 36776764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does the miR-105-1-Kisspeptin Axis Promote Ovarian Cell Functions?Reprod Sci. 2024 Aug;31(8):2293-2308. doi: 10.1007/s43032-024-01554-3. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Reprod Sci. 2024. PMID: 38632222 Free PMC article.
-
The human ATAD5 has evolved unique structural elements to function exclusively as a PCNA unloader.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Nov;31(11):1680-1691. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01332-4. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38871854 Free PMC article.
-
ATAD5-BAZ1B interaction modulates PCNA ubiquitination during DNA repair.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 3;15(1):10496. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55005-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39627214 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

