Mechanistic Understanding of Lanthipeptide Biosynthetic Enzymes
- PMID: 28135077
- PMCID: PMC5408752
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00591
Mechanistic Understanding of Lanthipeptide Biosynthetic Enzymes
Abstract
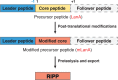
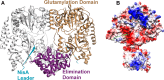
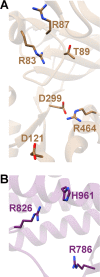
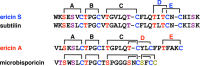
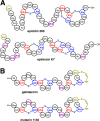
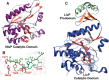
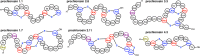
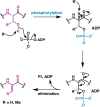
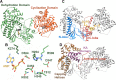
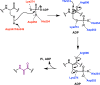
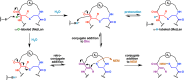
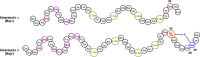
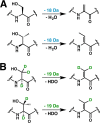
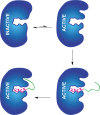
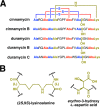
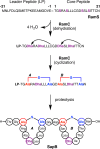
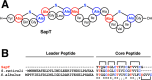
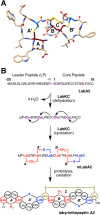
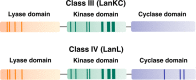
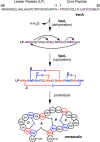
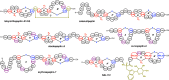
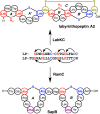
Lanthipeptides are ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) that display a wide variety of biological activities, from antimicrobial to antiallodynic. Lanthipeptides that display antimicrobial activity are called lantibiotics. The post-translational modification reactions of lanthipeptides include dehydration of Ser and Thr residues to dehydroalanine and dehydrobutyrine, a transformation that is carried out in three unique ways in different classes of lanthipeptides. In a cyclization process, Cys residues then attack the dehydrated residues to generate the lanthionine and methyllanthionine thioether cross-linked amino acids from which lanthipeptides derive their name. The resulting polycyclic peptides have constrained conformations that confer their biological activities. After installation of the characteristic thioether cross-links, tailoring enzymes introduce additional post-translational modifications that are unique to each lanthipeptide and that fine-tune their activities and/or stability. This review focuses on studies published over the past decade that have provided much insight into the mechanisms of the enzymes that carry out the post-translational modifications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures











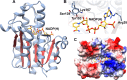


















References
-
- Arnison P. G.; Bibb M. J.; Bierbaum G.; Bowers A. A.; Bugni T. S.; Bulaj G.; Camarero J. A.; Campopiano D. J.; Challis G. L.; Clardy J.; et al. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30 (1), 108–160. 10.1039/C2NP20085F. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Park S.; James C. D. Lanthionine synthetase components C-like 2 increases cellular sensitivity to adriamycin by decreasing the expression of P-glycoprotein through a transcription-mediated mechanism. Cancer Res. 2003, 63 (3), 723–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

