The Influence of 17 Hours of Normobaric Hypoxia on Parallel Adjustments in Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Airway Function in Lowland Healthy Adults
- PMID: 28135110
- PMCID: PMC5361759
- DOI: 10.1089/ham.2016.0086
The Influence of 17 Hours of Normobaric Hypoxia on Parallel Adjustments in Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Airway Function in Lowland Healthy Adults
Abstract
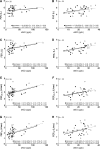
Van Iterson, Erik H., Eric M. Snyder, and Bruce D. Johnson. The influence of 17 hours of normobaric hypoxia on parallel adjustments in exhaled nitric oxide and airway function in lowland healthy adults. High Alt Med Biol. 18:1-10, 2017.-Currently, there is a disparate understanding of the role that normobaric hypoxia plays in affecting nitric oxide (NO) measured in exhaled air (eNO) and airway function in lowland healthy adults. Compared to normobaric normoxia, this study aimed to test the effect of 17 hours of normobaric hypoxia on relationships between eNO and airway function in healthy adults. In a crossover study including 2 separate visits, 26 lowland healthy Caucasian adults performed eNO and pulmonary function tests on visit 1 in normobaric normoxia, while repeating all tests on visit 2 following 17 hours of normobaric hypoxia (12.5% O2). Compared to normobaric normoxia, eNO (29 ± 24 vs. 36 ± 28 ppb), forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) (4.1 ± 0.7 vs. 4.3 ± 0.8 L), mean forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% FVC (FEF25-75) (3.9 ± 1.0 vs. 4.2 ± 1.2 L/s), and forced expiratory flow at 75% FVC (FEF75) (2.0 ± 0.7 vs. 2.3 ± 0.8 L/s) increased in normobaric hypoxia, respectively (all p < 0.05). Correlations at normoxia between eNO and FEV1 (r = 0.39 vs. 0.44), FEF25-75 (r = 0.51 vs. 0.51), and FEF75 (r = 0.53 vs. 0.55) persisted as both parameters increased in hypoxia, respectively. For the first time, these data suggest that 17 hours of hypoxic breathing in the absence of low ambient pressure contribute to increased eNO and airway function in lowland healthy adults.
Keywords: NO hypoxia; NOS hypoxia; altitude hypoxia; ambient pressure hypoxia; hypobaric hypoxia; pulmonary function hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors and/or study team members involved in this study do not have any competing financial interests to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electronic Cigarettes: Impact on Lung Function and Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Among Healthy Adults.Am J Mens Health. 2019 Jan-Feb;13(1):1557988318806073. doi: 10.1177/1557988318806073. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Am J Mens Health. 2019. PMID: 30318975 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-Analysis of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Acute Normobaric Hypoxia.Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2015 Aug;86(8):693-7. doi: 10.3357/AMHP.4172.2015. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2015. PMID: 26387892 Review.
-
The clinical value of exhaled nitric oxide in patients with lung cancer.Clin Respir J. 2018 Jan;12(1):23-30. doi: 10.1111/crj.12471. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 26934059
-
Sputum induction leads to a decrease of exhaled nitric oxide unrelated to airflow.Eur Respir J. 2003 Aug;22(2):354-7. doi: 10.1183/09031936.03.00118602. Eur Respir J. 2003. PMID: 12952273
-
Hypoxia and standing balance.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021 Apr;121(4):993-1008. doi: 10.1007/s00421-020-04581-5. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33484334 Review.
Cited by
-
Alveolar air and oxidative metabolic demand during exercise in healthy adults: the role of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the β2AR gene.Physiol Rep. 2017 Nov;5(20):e13476. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13476. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29061864 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Inhaled Amiloride on Lung Fluid Clearance in Response to Normobaric Hypoxia in Healthy Individuals.High Alt Med Biol. 2017 Dec;18(4):343-354. doi: 10.1089/ham.2017.0032. Epub 2017 Sep 6. High Alt Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28876128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American College of Sports Medicine. (2013). ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
-
- American Thoracic Society, and American College of Chest Physicians. (2003). ATS/ACCP statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:211–277 - PubMed
-
- Beckman JS, and Koppenol WH. (1996). Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol 271:C1424–C1437 - PubMed
-
- Busch T, Bartsch P, Pappert D, Grunig E, Hildebrandt W, Elser H, Falke KJ, and Swenson ER. (2001). Hypoxia decreases exhaled nitric oxide in mountaineers susceptible to high-altitude pulmonary edema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:368–373 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

