Women's knowledge and attitudes towards cervical cancer prevention: a cross sectional study in Eastern Uganda
- PMID: 28137260
- PMCID: PMC5282746
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-017-0365-3
Women's knowledge and attitudes towards cervical cancer prevention: a cross sectional study in Eastern Uganda
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among women in Uganda, often due to late disease diagnosis. Early screening for the cancer has been shown to be the most effective measure against the disease. Studies conducted elsewhere have reported the lack of awareness and negative attitudes towards cervical cancer as barriers to early screening. This study assessed the knowledge and attitudes of Ugandan women about cervical cancer prevention with the aim of informing prevention and control interventions.
Methods: This study was conducted in Bugiri and Mayuge districts in eastern Uganda. It was a cross-sectional community based survey and collected data by means of a questionnaire. A total of 900 women aged 25-49 years participated in the study. Women's knowledge and attitudes towards cervical cancer prevention were assessed and scored. Data were analysed using STATA 12.0 software. Bivariate and multivariate analyses were carried out to establish the relationship between knowledge levels and demographic characteristics.
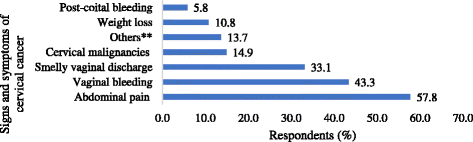
Results: Most (794; 88.2%) of the respondents had heard about cervical cancer, the majority (557; 70.2%) having received information from radio and 120 (15.1%) from health facilities. Most women (562; 62.4%) knew at least one preventive measure and (743; 82.6%) at least one symptom or sign of the disease. The majority (684; 76.0%) of respondents perceived themselves to be at risk of cervical cancer, a disease most (852; 94.6%) thought to be very severe. Living in peri-urban areas (AOR = 1.62, 95% CI: 1.15 - 2.28), urban areas (AOR = 3.64, 95% CI: 2.14 - 6.19), having a higher monthly income (AOR = 0.50, 95% CI: 0.37 - 0.68) and having had an HIV test (AOR = 1.99, 95% CI: 1.34-2.96) were associated with level of knowledge about cervical cancer prevention.
Conclusion: Although general knowledge about cervical cancer prevention was relatively high among women, and attitudes mostly encouraging, specific knowledge about screening was low. There were also undesirable perceptions and beliefs regarding cervical cancer among respondents. There is therefore need for more education campaigns to bridge identified knowledge gaps, and scale up of cervical cancer screening services to all women to increase service uptake.
Keywords: Attitudes; Cervical cancer; Knowledge; Prevention; Rural; Screening; Uganda.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uptake of Cervical Cancer Screening and Associated Factors among Women in Rural Uganda: A Cross Sectional Study.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0149696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149696. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26894270 Free PMC article.
-
Women's intention to screen and willingness to vaccinate their daughters against cervical cancer - a cross sectional study in eastern Uganda.BMC Public Health. 2017 Mar 14;17(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4180-4. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28288614 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and predictors of cervical cancer screening among HIV-positive women in rural western Uganda: insights from the health-belief model.BMC Cancer. 2023 Dec 8;23(1):1216. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11683-8. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38066496 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes, and practice of cervical cancer prevention among health workers in rural health centres of Northern Uganda.BMC Cancer. 2021 Feb 3;21(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07847-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33535977 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive knowledge on cervical cancer, attitude towards its screening and associated factors among women aged 30-49 years in Finote Selam town, northwest Ethiopia.Reprod Health. 2018 Feb 14;15(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12978-018-0471-1. Reprod Health. 2018. PMID: 29444689 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Perceptions of key informants on the provision of cervical cancer prevention and control programme in Uganda: implication for cervical cancer policy.BMC Public Health. 2020 Sep 14;20(1):1396. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09482-y. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32928155 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and Attitude of Adolescent Girls and Their Mothers Regarding Cervical Cancer: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study.J Midlife Health. 2018 Jul-Sep;9(3):145-149. doi: 10.4103/jmh.JMH_45_18. J Midlife Health. 2018. PMID: 30294187 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical cancer screening uptake and determinant factors among women in Ambo town, Western Oromia, Ethiopia: Community-based cross-sectional study.Cancer Med. 2021 Dec;10(23):8651-8661. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4369. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34704666 Free PMC article.
-
Uptake of Cervical Cancer Screening and Associated Factors among Women in Rural Uganda: A Cross Sectional Study.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0149696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149696. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26894270 Free PMC article.
-
Health communication in low-income countries: A 60-year bibliometric and thematic analysis.J Educ Health Promot. 2020 Jul 28;9:163. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_384_20. eCollection 2020. J Educ Health Promot. 2020. PMID: 32953895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart Bernard W, Wild Christopher P. World Cancer Report 2014. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization; 2014. - PubMed
-
- Cristina Herdman JS. Seattle Program for Appropriate Technology in Health (PATH) 2 2000. Planning appropriate cervical cancer prevention programs.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical