Seroprevalence and geographical distribution of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 among volunteer blood donors in endemic areas of Iran
- PMID: 28137274
- PMCID: PMC5282699
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-017-0693-9
Seroprevalence and geographical distribution of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 among volunteer blood donors in endemic areas of Iran
Abstract
Background: Human T-cell lymphotrophic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) has a worldwide distribution and it is endemic in some regions of Iran. One of the most important routes of HTLV-1 transmission is via transfusion of contaminated blood components. The risk of transmission through asymptomatic blood donors, particularly in endemic areas should be considered and appropriately managed. The main objective of this study was to determine the seroprevalence and description the geographic distribution of HTLV-1 among voluntary blood donors in Iran.
Methods: This retrospective study carried out using the data obtained from the main database of the seven blood transfusion centers of Iranian Blood Transfusion Organization between 2009 and 2013. The presence of anti-HTLV-1/2 antibodies were primarily assessed using Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay. The Ab Kit assay, contain antigens for the screening of antibodies to HTLV type 1 and 2. So, it is expressed as HTLV 1/2 assay. Samples that were positive by the western blot confirmatory test were considered as definite positive HTLV-1 or HTLV-2 cases. The main socio-demographic variables were; age, gender, donation history and marital status. Descriptive and analytical statistics were used to summarize the gathered data. The chi-Square Statistical test was used to test the association between groups, P-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
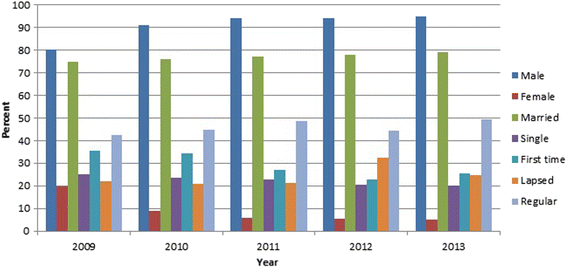
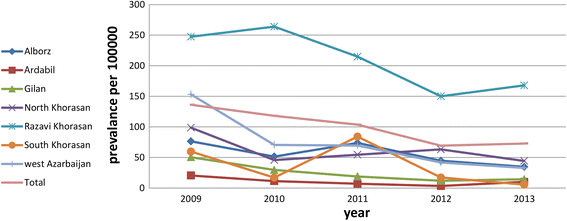
Results: A total of 1864489 blood donations were evaluated. There were 1840 confirmed HTLV-1 positive donations (0.098%). None were positive for anti-HTLV-2. The overall HTLV-1 prevalence was 98.7 per 100,000 donations during the 5 year period. Seroprevalence was higher among females, married and older blood donors. The overall seropositivity among first time, regular and lapsed donors was, 0.29% (290/100000), 0.001% (1/100000) and 0.02% (20/100000) respectively. A significant difference was observed between regular and the first time (p <0.0001) and also between lapsed and regular blood donors (p <0.0001). Most of the HTLV-1 seropositive blood donors (175 per 100,000) were from northeastern regions. We observed a gradual decline in overall HTLV-1 prevalence during the course of the study, the prevalence rate decreased from 0.13% (130/100000) in 2009 to 0.07% (70/100000) in 2013.
Conclusions: The Seroprevalence of HTLV-1 among Iranian blood donors in the regions of our study still is considerable, but there is an obvious declining prevalence over the course of present study. Blood transfusion centers should continually evaluate the residual risk of infection in the country, especially in endemic areas.
Keywords: Blood donation; Blood donors; HTLV-1; Seroepidemiologic studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type I (HTLV-1) Infection among Iranian Blood Donors: First Case-Control Study on the Risk Factors.Viruses. 2015 Nov 4;7(11):5736-45. doi: 10.3390/v7112904. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26556363 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 and 2 Seroprevalence among first-time blood donors in Chile, 2011-2013.J Med Virol. 2016 Jun;88(6):1067-75. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24428. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Med Virol. 2016. PMID: 26538335
-
[Determination of anti-HTLV-I/II antibodies: Experience in 28,897 blood donations in Buenos Aires].Sangre (Barc). 1995 Dec;40(6):447-51. Sangre (Barc). 1995. PMID: 8850226 Spanish.
-
Seroprevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) in blood donors in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Vox Sang. 2019 Jul;114(5):413-425. doi: 10.1111/vox.12779. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Vox Sang. 2019. PMID: 30972789
-
Serological and Molecular Methods to Study Epidemiological Aspects of Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 Infection.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1582:3-24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6872-5_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28357658 Review.
Cited by
-
Fine-scale geographic clustering pattern of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection among blood donors in Kyushu-Okinawa, Japan.J Med Virol. 2018 Oct;90(10):1658-1665. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25239. Epub 2018 Jul 10. J Med Virol. 2018. PMID: 29900555 Free PMC article.
-
Serologic screening for viral infections among blood donors: a study in a blood bank in southern Brazil.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024 Sep 2;70(8):e20240452. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20240452. eCollection 2024. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024. PMID: 39230147 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of molecular epidemiologic pattern of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) in Alborz province, Iran.Virus Genes. 2024 Apr;60(2):117-125. doi: 10.1007/s11262-024-02051-0. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Virus Genes. 2024. PMID: 38273115
-
Seroprevalence of Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus Types I/II Among Blood Donors in a Tertiary Hospital in Oman.Oman Med J. 2024 Jan 31;39(1):e587. doi: 10.5001/omj.2024.42. eCollection 2024 Jan. Oman Med J. 2024. PMID: 38572398 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on the Epidemiology of the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Infection in the Countries of the Eastern Mediterranean Regional Office of the World Health Organization with Special Emphasis on the Situation in Iran.Viruses. 2022 Mar 23;14(4):664. doi: 10.3390/v14040664. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farid R, Etemadi M, Baradaran H, Nikbin B. Seroepidemiology and virology of HTLV-1 in the city of Mashhad, northeastern Iran. Serodiagn Immunother Infect Dis. 1993;5:251–2. doi: 10.1016/0888-0786(93)90011-N. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources