Case report: when two and ½ men go camping…
- PMID: 28137306
- PMCID: PMC5282854
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2213-3
Case report: when two and ½ men go camping…
Abstract
Background: In patients, rapid identification of bacterial species may help to guide treatment at early stages. New protocols for the identification directly from positive blood culture flasks significantly helped in the presented case report.
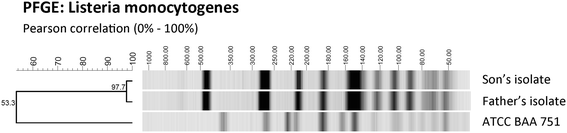
Case presentation: Two patients (a father and son) presented with diarrhea, malaise, and fever of 3 to 4 days duration. Blood cultures from both patients cultured short Gram-positive rods. MALDI-TOF based rapid identification protocol direct from positive blood culture identified Listeria monocytogenes as the cause of sepsis and could be confirmed with conventional methods. Listeria monocytogenes was identified 24 h later by conventional biochemical identification methods (VITEK 2). Antibiotic treatment was adjusted early in response to the MALDI-TOF based identification of bacteremia. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis confirmed the suspected relatedness of the father's and son's isolates.
Conclusions: MALDI-TOF based may provide a rapid identification of bacterial species directly from positive blood culture.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes; MALDI-TOF; Pulsed field gel electrophoresis; Rapid identification; Sepsis; Typing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid identification and source-tracking of Listeria monocytogenes using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 Jun 2;202:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.01.023. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25747262
-
Rapid identification and typing of listeria species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Sep;74(17):5402-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02689-07. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18606788 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Impact of Rapid, Direct MALDI-ToF Identification of Bacteria from Positive Blood Cultures.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 30;11(12):e0169332. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169332. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28036369 Free PMC article.
-
[Use of MALDI-TOF in the rapid diagnosis of sepsis].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2016 Jun;34 Suppl 2:19-25. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(16)30186-0. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2016. PMID: 27389288 Review. Spanish.
-
[Bacteraemia due to L. monocytogenes: Description of cases and review of literature].Rev Esp Geriatr Gerontol. 2020 Jan-Feb;55(1):50-53. doi: 10.1016/j.regg.2019.05.007. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Rev Esp Geriatr Gerontol. 2020. PMID: 31521408 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
How MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Technology Contributes to Microbial Infection Control in Healthcare Settings.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 8;10(11):1881. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111881. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A life-devastating cause of gastroenteritis in an immunocompetent host: was it suspected?Clin Case Rep. 2017 Dec 15;6(1):209-213. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.1338. eCollection 2018 Jan. Clin Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29375867 Free PMC article.
-
Successfully treated infected aneurysm caused by Listeria monocytogenes.IDCases. 2021 Jun 26;25:e01206. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2021.e01206. eCollection 2021. IDCases. 2021. PMID: 34258224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gesundheit BF. Wöchentliche Fallzahlen, Meldungen Infektionskrankheiten. BAG Bulletin; 2015
-
- Gesundheit Bf Die Listeriose in der Schweiz - Empfehlungen zu Prävention, Diagnose und Therapie. BAG Bulletin. 2001;41:773–775.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical