Transcriptional, Functional, and Mechanistic Comparisons of Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocytes, HepaRG Cells, and Three-Dimensional Human Hepatocyte Spheroids as Predictive In Vitro Systems for Drug-Induced Liver Injury
- PMID: 28137721
- PMCID: PMC5363699
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.116.074369
Transcriptional, Functional, and Mechanistic Comparisons of Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocytes, HepaRG Cells, and Three-Dimensional Human Hepatocyte Spheroids as Predictive In Vitro Systems for Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Abstract
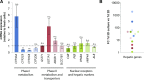
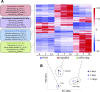
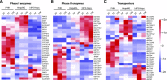
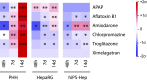
Reliable and versatile hepatic in vitro systems for the prediction of drug pharmacokinetics and toxicity are essential constituents of preclinical safety assessment pipelines for new medicines. Here, we compared three emerging cell systems-hepatocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells, HepaRG cells, and three-dimensional primary human hepatocyte (PHH) spheroids-at transcriptional and functional levels in a multicenter study to evaluate their potential as predictive models for drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Transcriptomic analyses revealed widespread gene expression differences between the three cell models, with 8148 of 17,462 analyzed genes (47%) being differentially expressed. Expression levels of genes involved in the metabolism of endogenous as well as xenobiotic compounds were significantly elevated in PHH spheroids, whereas genes involved in cell division and endocytosis were significantly upregulated in HepaRG cells and hepatocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells, respectively. Consequently, PHH spheroids were more sensitive to a panel of drugs with distinctly different toxicity mechanisms, an effect that was amplified by long-term exposure using repeated treatments. Importantly, toxicogenomic analyses revealed that transcriptomic changes in PHH spheroids were in compliance with cholestatic, carcinogenic, or steatogenic in vivo toxicity mechanisms at clinically relevant drug concentrations. Combined, the data reveal important phenotypic differences between the three cell systems and suggest that PHH spheroids can be used for functional investigations of drug-induced liver injury in vivo in humans.
Copyright © 2017 by The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Anderson N, Borlak J. (2006) Drug-induced phospholipidosis. FEBS Lett 580:5533–5540. - PubMed
-
- Anthérieu S, Rogue A, Fromenty B, Guillouzo A, Robin MA. (2011) Induction of vesicular steatosis by amiodarone and tetracycline is associated with up-regulation of lipogenic genes in HepaRG cells. Hepatology 53:1895–1905. - PubMed
-
- Ayd FJ., Jr (1956) The dermatologic and systemic manifestations of chlorpromazine hypersensitivity; their clinical significance and management. J Nerv Ment Dis 124:84–87. - PubMed
-
- Bates DW, Spell N, Cullen DJ, Burdick E, Laird N, Petersen LA, Small SD, Sweitzer BJ, Leape LL, Adverse Drug Events Prevention Study Group (1997) The costs of adverse drug events in hospitalized patients. JAMA 277:307–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

