Importance of the Exopolysaccharide Matrix in Antimicrobial Tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aggregates
- PMID: 28137803
- PMCID: PMC5365683
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02696-16
Importance of the Exopolysaccharide Matrix in Antimicrobial Tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aggregates
Abstract
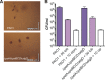
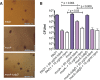
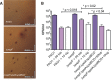
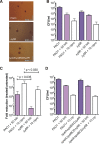
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen that can infect the lungs of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients and persist in the form of antibiotic-tolerant aggregates in the mucus. It has recently been suggested that such aggregates are formed due to restricted bacterial motility independent of the production of extracellular matrix components, and that they do not rely on an extracellular matrix for antimicrobial tolerance. However, we show here that biofilm matrix overexpression, as displayed by various clinical isolates, significantly protects P. aeruginosa aggregates against antimicrobial treatment. Alginate-overproducing mucA mutant bacteria growing in aggregates showed highly increased antibiotic tolerance compared to wild-type bacteria in aggregates. Deletion of algD in the mucA mutant strain abrogated alginate production and reversed the antibiotic tolerance displayed by the aggregates to a level similar to that observed for aggregates formed by the wild type. The P. aeruginosa ΔwspF and ΔyfiR mutant strains both overproduce Pel and Psl exopolysaccharide, and when these bacteria grew in aggregates, they showed highly increased antibiotic tolerance compared to wild-type bacteria growing in aggregates. However, the ΔwspF and ΔyfiR mutant strains, deficient in Pel/Psl production due to additional ΔpelA ΔpslBCD deletions, formed aggregates that displayed antibiotic tolerance levels close to those of wild-type aggregates. These results suggest that biofilm matrix components, such as alginate, Pel, and Psl, do play a role in the tolerance toward antimicrobials when bacteria grow as aggregates.
Keywords: aggregates; antimicrobial tolerance; biofilm; extracellular matrix.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Can Produce Calcium-Gelled Biofilms Independent of the Matrix Components Psl and CdrA.J Bacteriol. 2022 May 17;204(5):e0056821. doi: 10.1128/jb.00568-21. Epub 2022 Apr 13. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35416688 Free PMC article.
-
The Versatile Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Matrix Protein CdrA Promotes Aggregation through Different Extracellular Exopolysaccharide Interactions.J Bacteriol. 2020 Sep 8;202(19):e00216-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00216-20. Print 2020 Sep 8. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32661078 Free PMC article.
-
The role of exopolysaccharides Psl and Pel in resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the oxidative stressors sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0092224. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00922-24. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39194290 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Biofilm Exopolysaccharide Biosynthesis and Degradation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2022 Sep 8;76:413-433. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-041320-111355. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35655342 Review.
-
Role of polysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Dec;10(6):644-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.09.010. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17981495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interference of Lactobacillus casei with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the treatment of infected burns in Wistar rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021 Feb;24(2):143-149. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2020.47447.10920. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33953852 Free PMC article.
-
The Innate Immune Protein Calprotectin Interacts With and Encases Biofilm Communities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 13;12:898796. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.898796. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35909964 Free PMC article.
-
The Inoculation Method Could Impact the Outcome of Microbiological Experiments.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Feb 14;84(5):e02264-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02264-17. Print 2018 Mar 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29269495 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Beta Lactam Antibiotics for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections in Children: A Narrative Review.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 13;11(7):1798. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071798. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerance and Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms to Antimicrobial Agents-How P. aeruginosa Can Escape Antibiotics.Front Microbiol. 2019 May 3;10:913. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00913. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31130925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tseng BS, Zhang W, Harrison JJ, Quach TP, Song JL, Penterman J, Singh PK, Chopp DL, Packman AI, Parsek MR. 2013. The extracellular matrix protects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by limiting the penetration of tobramycin. Environ Microbiol 15:2865–2878. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12155. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

