Effects of Tedizolid Phosphate on Survival Outcomes and Suppression of Production of Staphylococcal Toxins in a Rabbit Model of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Necrotizing Pneumonia
- PMID: 28137816
- PMCID: PMC5365717
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02734-16
Effects of Tedizolid Phosphate on Survival Outcomes and Suppression of Production of Staphylococcal Toxins in a Rabbit Model of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Necrotizing Pneumonia
Abstract
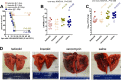
The protective efficacy of tedizolid phosphate, a novel oxazolidinone that potently inhibits bacterial protein synthesis, was compared to those of linezolid, vancomycin, and saline in a rabbit model of Staphylococcus aureus necrotizing pneumonia. Tedizolid phosphate was administered to rabbits at 6 mg/kg of body weight intravenously twice daily, which yielded values of the 24-h area under the concentration-time curve approximating those found in humans. The overall survival rate was 83% for rabbits treated with 6 mg/kg tedizolid phosphate twice daily and 83% for those treated with 50 mg/kg linezolid thrice daily (P = 0.66 by the log-rank test versus the results obtained with tedizolid phosphate). These survival rates were significantly greater than the survival rates of 17% for rabbits treated with 30 mg/kg vancomycin twice daily (P = 0.003) and 17% for rabbits treated with saline (P = 0.002). The bacterial count in the lungs of rabbits treated with tedizolid phosphate was significantly decreased compared to that in the lungs of rabbits treated with saline, although it was not significantly different from that in the lungs of rabbits treated with vancomycin or linezolid. The in vivo bacterial production of alpha-toxin and Panton-Valentine leukocidin, two key S. aureus-secreted toxins that play critical roles in the pathogenesis of necrotizing pneumonia, in the lungs of rabbits treated with tedizolid phosphate and linezolid was significantly inhibited compared to that in the lungs of rabbits treated with vancomycin or saline. Taken together, these results indicate that tedizolid phosphate is superior to vancomycin for the treatment of S. aureus necrotizing pneumonia because it inhibits the bacterial production of lung-damaging toxins at the site of infection.
Keywords: PVL; alpha-toxin; linezolid; pneumonia; rabbit model; tedizolid; vancomycin.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of linezolid on suppressing in vivo production of staphylococcal toxins and improving survival outcomes in a rabbit model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus necrotizing pneumonia.J Infect Dis. 2013 Jul;208(1):75-82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit129. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23532096 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacies of tedizolid phosphate, vancomycin, and daptomycin in a rabbit model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(6):3252-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04376-14. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25801564 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacies of Tedizolid Phosphate, Linezolid, and Vancomycin in a Murine Model of Subcutaneous Catheter-Related Biofilm Infection Due to Methicillin-Susceptible and -Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jul 22;60(8):5092-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00880-16. Print 2016 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27297485 Free PMC article.
-
Tedizolid: a novel oxazolidinone with potent activity against multidrug-resistant gram-positive pathogens.Drugs. 2015 Feb;75(3):253-70. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0352-7. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25673021 Review.
-
Early experience with tedizolid: clinical efficacy, pharmacodynamics, and resistance.Pharmacotherapy. 2014 Nov;34(11):1198-208. doi: 10.1002/phar.1491. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Pharmacotherapy. 2014. PMID: 25266820 Review.
Cited by
-
Community-acquired Pneumonia with Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in a Patient Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: A Therapeutic Challenge.Cureus. 2018 Jan 3;10(1):e2019. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2019. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 29531872 Free PMC article.
-
Tedizolid phosphate for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy.Core Evid. 2019 Jul 5;14:31-40. doi: 10.2147/CE.S187499. eCollection 2019. Core Evid. 2019. PMID: 31308835 Free PMC article.
-
Best Practices in the Development and Use of Experimental Models of Bacterial Pneumonia: An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025 Aug;73(2):178-199. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2025-0322ST. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40748059 Free PMC article.
-
Subinhibitory concentrations of tedizolid potently inhibit extracellular toxin production by methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Med Microbiol. 2019 Feb;68(2):255-262. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000905. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30556803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moran GJ, Fang E, Corey GR, Das AF, De Anda C, Prokocimer P. 2014. Tedizolid for 6 days versus linezolid for 10 days for acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections (ESTABLISH-2): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis 14:696–705. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70737-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bolz DD, Katahira EJ, Bryant AE, Stevens DL. 2016. Subinhibitory concentrations of tedizolid effectively inhibit extracellular toxin production by methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Open Forum Infect Dis 3(suppl_1):2052. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofw172.1600. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, Rybak MJ, Talan DA, Chambers HF. 2011. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children: executive summary. Clin Infect Dis 52:285–292. doi:10.1093/cid/cir034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Diep BA, Chan L, Tattevin P, Kajikawa O, Martin TR, Basuino L, Mai TT, Marbach H, Braughton KR, Whitney AR, Gardner DJ, Fan X, Tseng CW, Liu GY, Badiou C, Etienne J, Lina G, Matthay MA, DeLeo FR, Chambers HF. 2010. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes mediate Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin-induced lung inflammation and injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:5587–5592. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912403107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

