IgD class switching is initiated by microbiota and limited to mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in mice
- PMID: 28137874
- PMCID: PMC5321007
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1621258114
IgD class switching is initiated by microbiota and limited to mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in mice
Abstract
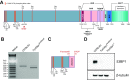
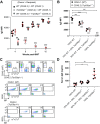
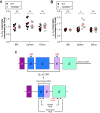
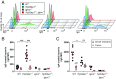
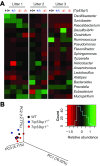
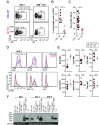
Class-switch recombination (CSR) alters the Ig isotype to diversify antibody effector functions. IgD CSR is a rare event, and its regulation is poorly understood. We report that deficiency of 53BP1, a DNA damage-response protein, caused age-dependent overproduction of secreted IgD resulting from increased IgD CSR exclusively within B cells of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues. IgD overproduction was dependent on activation-induced cytidine deaminase, hematopoietic MyD88 expression, and an intact microbiome, against which circulating IgD, but not IgM, was reactive. IgD CSR occurred via both alternative nonhomologous end-joining and homologous recombination pathways. Microbiota-dependent IgD CSR also was detected in nasal-associated lymphoid tissue of WT mice. These results identify a pathway, present in WT mice and hyperactivated in 53BP1-deficient mice, by which microbiota signal via Toll-like receptors to elicit IgD CSR.
Keywords: 53BP1; IgD; Toll-like receptor; class-switch recombination; microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Comment in
-
Microbiome-dependent recombination shapes the host antibody repertoire.Sci Signal. 2017 Feb 21;10(467):eaan0005. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aan0005. Sci Signal. 2017. PMID: 28223410
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

