Asenapine for the Control of Physical Aggression: A Prospective Naturalist Pilot Study
- PMID: 28138201
- PMCID: PMC5274528
- DOI: 10.64719/pb.4353
Asenapine for the Control of Physical Aggression: A Prospective Naturalist Pilot Study
Abstract
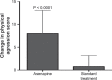
It has been previously purported that higher relative affinity to the dopamine D4 receptor compared to D2 (i.e., D4/D2 affinity ratio > 1) may underlie unique antiaggression potency. Asenapine is a newer antipsychotic that also has D4/D2 affinity ratio > 1. It has demonstrated efficacy in reducing acute agitation in a placebo-controlled study. We performed a prospective naturalistic, pilot, proof of concept study on an inpatient psychiatric unit. Among patients with aggression at time of admission (≥ 12 on Refined Aggression Questionnaire [RAQ], or ≥ 2 on Modified Overt Aggression Scale [MOAS]), asenapine treatment was associated with a significant reduction in total aggression as measured by the MOAS (-14.7 ± 11.59 vs. -5.4 ± 10.12, P = 0.045), and particularly physical aggression (-8.0 ± 5.06 vs. -0.78 ± 2.40, P < 0.0001) compared to treatment that did not include asenapine. These data suggest that asenapine may be useful in the targeted treatment of aggression, and provide some support for the D4/D2 affinity ratio hypothesis.
Keywords: aggression; asenapine; dopamine receptors; physical aggression; treatment; violence.
Copyright © 1964–2017 by MedWorks Media Inc, Los Angeles, CA All rights reserved. Printed in the United States.
Figures
References
-
- Schuepbach D, Goetz I, Boeker H, Hell D. Voluntary vsinvoluntary hospital admission in acute mania of bipolar disorder: Results from the Swiss sample of the EMBLEM study. J Affect Disord. 2006;90:57–61. - PubMed
-
- Comai S, Tau M, Gobbi G. The psychopharmacology of aggressive behavior: a translational approach: part 1: neurobiology. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012;32(1):83–94. - PubMed
-
- Comai S, Tau M, Pavlovic Z, Gobbi G. The psychopharmacology of aggressive behavior: a translational approach. Part 2: Clinical studies using atypical antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, and lithium. J Clin Psychopharmacology. 2012;32(2):237–260. - PubMed
-
- Frogley C, Taylor D, Dickens G, Picchioni M. A systematic review of the evidence of clozapine’s anti-aggressive effects. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012;20:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Essock SM, Frisman LK, Covell NH, Hargreaves W. Cost-effectiveness of clozapine compared with conventional antipsychotic medications for patients in state hospitals. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:987–994. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources