Detection of Intestinal Pathogens in River, Shore, and Drinking Water in Lima, Peru
- PMID: 28138344
- PMCID: PMC5278651
- DOI: 10.7150/jgen.18378
Detection of Intestinal Pathogens in River, Shore, and Drinking Water in Lima, Peru
Abstract
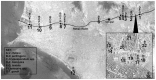
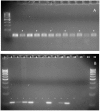
Water quality management is an ongoing struggle for many locations worldwide. Current testing of water supplies can be time-consuming, expensive, and lack sensitivity. This study describes an alternative, easy-to-use, and inexpensive method to water sampling and testing at remote locations. This method was employed to detect a number of intestinal pathogens in various locations of Lima, Peru. A total of 34 PCR primer pairs were tested for specificity and high-yield amplification for 12 different pathogens using known DNA templates. Select primers for each pathogen were then tested for minimum detection limits of DNA. Water samples were collected from 22 locations. PCR was used to detect the presence of a pathogen, virulence factors, or differentiate between pathogenic species. In 22 water samples, cholera toxin gene was detected in 4.5% of samples, C. perfringens DNA was detected in 50% of samples, E. histolytica DNA was detected in 54.5% of samples, Giardia intestinalis DNA was detected in 4.5% of samples, Leptospira spp. DNA was detected in 29% of samples, and T. gondii DNA was detected in 31.8% of samples. DNA from three pathogens, C. perfringens, E. histolytica, and T. gondii, were found in residential samples, which accounted for 10 out of 22 samples.
Keywords: gel electrophoresis.; polymerase chain reaction (PCR); water sampling; water-borne pathogen detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection and differentiation of Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia, and Salmonella spp. in the municipality-supplied drinking water.J Lab Physicians. 2019 Jul-Sep;11(3):275-280. doi: 10.4103/JLP.JLP_66_18. J Lab Physicians. 2019. PMID: 31579243 Free PMC article.
-
The River Ruhr - an urban river under particular interest for recreational use and as a raw water source for drinking water: The collaborative research project "Safe Ruhr" - microbiological aspects.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2016 Oct;219(7 Pt B):643-661. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 27495908
-
Occurrence and molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts in raw water samples from the Rímac River, Peru.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Apr;25(12):11454-11467. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1423-6. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29423699
-
Is real-time PCR-based diagnosis similar in performance to routine parasitological examination for the identification of Giardia intestinalis, Cryptosporidium parvum/Cryptosporidium hominis and Entamoeba histolytica from stool samples? Evaluation of a new commercial multiplex PCR assay and literature review.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016 Feb;22(2):190.e1-190.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.10.019. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 26548509 Review.
-
[New methods for the diagnosis of Cryptosporidium and Giardia].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):151-5. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305706 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
From the Andes to the desert: 16S rRNA metabarcoding characterization of aquatic bacterial communities in the Rimac river, the main source of water for Lima, Peru.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 22;16(4):e0250401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250401. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33886647 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies among Patients with Cancer at Hiwa Cancer Hospital in Sulaimani City, Kurdistan Region, Iraq.Iran J Parasitol. 2023 Oct-Dec;18(4):526-534. doi: 10.18502/ijpa.v18i4.14261. Iran J Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 38169672 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Toxoplasma gondii inhibitor chemotypes.Parasitol Int. 2018 Apr;67(2):107-111. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2017.10.010. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Parasitol Int. 2018. PMID: 29081387 Free PMC article.
-
Neurological and Neurobehavioral Disorders Associated with Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Humans.J Parasitol Res. 2021 Oct 19;2021:6634807. doi: 10.1155/2021/6634807. eCollection 2021. J Parasitol Res. 2021. PMID: 34712493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vibrio cholerae in Water Environments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2025 Jun;17(3):e70103. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.70103. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40437911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

