Hospital clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus are carried by medical students even before healthcare exposure
- PMID: 28138384
- PMCID: PMC5260124
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-017-0175-2
Hospital clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus are carried by medical students even before healthcare exposure
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains are prevalent in healthcare and the community. Few studies have examined MRSA carriage among medical students. The aim of this study is to examine Staphylococcus aureus (SA) carriage, and particular MRSA, over time in cohort medical students.
Methods: Prospective collection of nasal swabs from medical students in Israel and assessment of SA carriage. Three samples were taken per student in preclinical and clinical parts of studies. Antibiotic susceptibilities were recorded and MRSA typing was performed by staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) types, Panton Valentine Leukocidin (PVL) encoding genes, and spa types. Clonality was assessed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
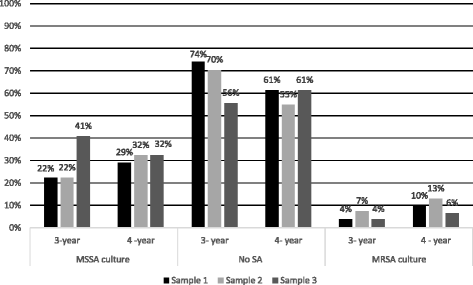
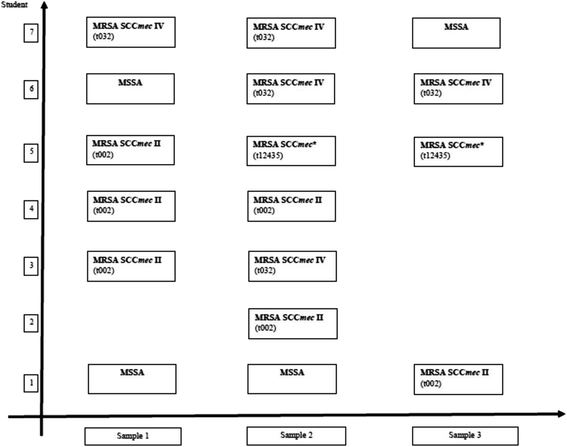
Results: Among 58 students, SA carriage rates increased from 33% to 38% to 41% at baseline (preclinical studies), 13 and 19 months (clinical studies), respectively (p = 0.07). Methicillin-susceptible SA (MSSA) carriage increased in the clinical studies period (22 to 41%, p = 0.01). Overall, seven students (12%) carried 13 MRSA isolates. MRSA isolates were PVL negative and were characterized as SCCmecII-t002, SCCmecIV-t032, or t12435 with untypable SCCmec. MRSA carriage during the pre-clinical studies was evident in 4/7 students. Two students carried different MRSA clones at various times and persistent MRSA carriage was noted in one student. Simultaneous carriage of MRSA and MSSA was not detected.
Conclusions: MSSA carriage increased during the clinical part of studies in Israeli medical students. Compared with previous reports, higher rates of MRSA carriage were evident. MRSA strains were genotypically similar to Israeli healthcare-associated clones; however, carriage occurred largely before healthcare exposure, implying community-acquisition of hospital strains.
Keywords: Carriage; Community-associated; Healthcare-associated; Medical students; Methicillin-resistance; Review; Staphylococcus aureus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from nasal samples of sixth year medical students during their pediatric services practices.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021 Apr 17;20(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12941-021-00429-8. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021. PMID: 33865424 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus nasal isolates from medical students in Cartagena, Colombia.Braz J Infect Dis. 2012 Jul-Aug;16(4):329-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2012.06.017. Braz J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22846119
-
Typing of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-encoding phages carried by methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Italy.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014 Nov;20(11):O840-6. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12679. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24835735
-
The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2008 Dec;8(6):747-63. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18718557 Review.
-
The molecular evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007 Mar;13(3):222-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01573.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 17391376 Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidics for the rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus using antibody-coated microspheres.Bioengineered. 2020 Dec;11(1):1137-1145. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2020.1831362. Bioengineered. 2020. PMID: 33070676 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of resistance to selected antibiotics and Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive Staphylococcus aureus in a healthy student population at a Malaysian University.Germs. 2018 Mar 1;8(1):21-30. doi: 10.18683/germs.2018.1129. eCollection 2018 Mar. Germs. 2018. PMID: 29564245 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from nasal samples of sixth year medical students during their pediatric services practices.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021 Apr 17;20(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12941-021-00429-8. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021. PMID: 33865424 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between the exposure to healthcare settings and colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among medical students.Germs. 2020 Mar 2;10(1):34-43. doi: 10.18683/germs.2020.1183. eCollection 2020 Mar. Germs. 2020. PMID: 32274358 Free PMC article.
-
Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus among Portuguese nursing students: A longitudinal cohort study over four years of education.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 30;12(11):e0188855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188855. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29190721 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

