The Impact of CB2 Receptor Ligands on the MK-801-Induced Hyperactivity in Mice
- PMID: 28138895
- PMCID: PMC5360834
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-017-9702-4
The Impact of CB2 Receptor Ligands on the MK-801-Induced Hyperactivity in Mice
Abstract
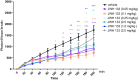
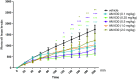
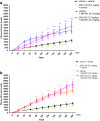
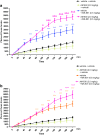
It has been known that there is a relationship between cannabis use and schizophrenia-related symptoms; however, it can be a subject of controversy. The involvement of CB1 receptor ligands in the schizophrenia has already been revealed and confirmed. However, there is still lack of information concerning the role of CB2 receptors in the psychosis-like effects in mice and the further studies are needed.The aim of the present research was to study the role of the CB2 receptor ligands in the symptoms typical for schizophrenia. We provoked hyperlocomotion in mice which is analogous to positive psychosis-like effects in humans, by an acute administration of a NMDA receptor antagonist, MK-801 (0.3 and 0.6 mg/kg), a pharmacological model of schizophrenia. An acute administration of MK-801 induced the increase in locomotor activity (hyperactivity) in rodents, measured in actimeters.We revealed that an acute injection of CB2 receptor agonist JWH 133 at the dose range (0.05-1.0 mg/kg) and CB2 receptor antagonist, AM 630 at the dose range (0.1-1.0 mg/kg) decreased locomotion of mice. An acute injection of JWH 133 (2.0 mg/kg) and AM 630 (2.0 mg/kg) had no statistical significant influence on the locomotor activity of mice. However, an acute injection of both CB2 receptor ligands (agonist and antagonist), JWH 133, at the non-effective dose of 2.0 mg/kg and AM 630 at the non-effective dose of 2.0 mg/kg, potentiated the MK-801-induced hyperactivity.The present findings have confirmed that endocannabinoid system, not only via CB1, but also via CB2 receptors, may be involved in the schizophrenia-like responses, including hyperlocomotion in mice.
Keywords: CB2 receptor ligands; Cannabis use; Endocannabinoid system; MK-801; Mice; Schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All experiments were conducted according to the National Institute of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and to the European Community Council Directive for the Care and Use of laboratory animals of 22 September 2010 (2010/63/EU), and approved by the local ethics committee. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from all individual participants for whom identifying information is included in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Influence of the CB1 Receptor Ligands on the Schizophrenia-Like Effects in Mice Induced by MK-801.Neurotox Res. 2016 Nov;30(4):658-676. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9662-0. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 27577742 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant-like effects of the cannabinoid receptor ligands in the forced swimming test in mice: mechanism of action and possible interactions with cholinergic system.Behav Brain Res. 2015 May 1;284:24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.01.051. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25660201
-
CB2 receptor agonism reverses MK-801-induced disruptions of prepulse inhibition in mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Aug;231(16):3071-87. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3481-x. Epub 2014 Apr 5. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24705902
-
Cannabinoids in pain management: CB1, CB2 and non-classic receptor ligands.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Aug;23(8):1123-40. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.918603. Epub 2014 May 16. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24836296 Review.
-
Cannabis and cannabinoids: pharmacology and rationale for clinical use.Forsch Komplementarmed. 1999 Oct;6 Suppl 3:12-5. doi: 10.1159/000057150. Forsch Komplementarmed. 1999. PMID: 10575283 Review.
Cited by
-
Endocannabinoid System Components as Potential Biomarkers in Psychiatry.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 27;11:315. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00315. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32395111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Indirect and Direct Modulation of Endocannabinoid System Function on Anxiety-Related Behavior in Mice Assessed in the Elevated Plus Maze Test.Molecules. 2025 Feb 13;30(4):867. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040867. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005177 Free PMC article.
-
GLYX-13 Ameliorates Schizophrenia-Like Phenotype Induced by MK-801 in Mice: Role of Hippocampal NR2B and DISC1.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Apr 11;11:121. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00121. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29695955 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Findings Guiding the Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System as a Potential Target to Treat Schizophrenia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1400:89-103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-97182-3_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35930228
-
Functional characterization of the cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 in zebrafish larvae using behavioral analysis.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jul;236(7):2049-2058. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05193-4. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30820632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida V, Peres FF, Levin R, Suiama MA, Calzavara MB, Zuardi AW, Hallak JE, Crippa JA, Abílio VC. Effects of cannabinoid and vanilloid drugs on positive and negative-like symptoms on an animal model of schizophrenia: the SHR strain. Schizophr Res. 2014;153(1–3):150–159. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.01.039. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

