Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in endothelium-independent relaxation to raloxifene in rat aorta
- PMID: 28138957
- PMCID: PMC5368050
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13733
Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in endothelium-independent relaxation to raloxifene in rat aorta
Abstract
Background and purpose: Raloxifene can induce both endothelium-dependent and -independent relaxation in different arteries. However, the underlying mechanisms by which raloxifene triggers endothelium-independent relaxation are still incompletely understood. The purpose of present study was to examine the roles of NOSs and Ca2+ channels in the relaxant response to raloxifene in the rat isolated, endothelium-denuded aorta.
Experimental approach: Changes in isometric tension, cGMP, nitrite, inducible NOS protein expression and distribution in response to raloxifene in endothelium-denuded aortic rings were studied by organ baths, radioimmunoassay, Griess reaction, western blot and immunohistochemistry respectively.
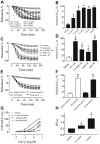
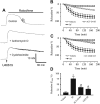
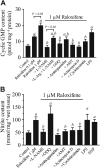
Key results: Raloxifene reduced the contraction to CaCl2 in a Ca2+ -free, high K+ -containing solution in intact aortic rings. Raloxifene also acutely relaxed the aorta primarily through an endothelium-independent mechanism involving NO, mostly from inducible NOS (iNOS) in vascular smooth muscle layers. This effect of raloxifene involved the generation of cGMP and nitrite. Also, it was genomic in nature, as it was inhibited by a classical oestrogen receptor antagonist and inhibitors of RNA and protein synthesis. Raloxifene-induced stimulation of iNOS gene expression was partly mediated through activation of the NF-κB pathway. Raloxifene was more potent than 17β-estradiol or tamoxifen at relaxing endothelium-denuded aortic rings by stimulation of iNOS.
Conclusions and implications: Raloxifene-mediated vasorelaxation in rat aorta is independent of a functional endothelium and is mediated by oestrogen receptors and NF-κB. This effect is mainly mediated through an enhanced production of NO, cGMP and nitrite, via the induction of iNOS and inhibition of calcium influx through Ca2+ channels in rat aortic smooth muscle.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




Comment in
-
Rapid vasodilation to raloxifene: role of oestrogen receptors and off-target effects.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;174(22):4201-4202. doi: 10.1111/bph.14020. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28983907 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Raloxifene relaxes rat pulmonary arteries and veins: roles of gender, endothelium, and antagonism of Ca2+ influx.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Mar;312(3):1266-71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.077990. Epub 2004 Nov 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15550571
-
Effect of 17beta-oestradiol on cytokine-induced nitric oxide production in rat isolated aorta.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Mar;123(6):1089-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701715. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9559891 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelium-independent relaxation to raloxifene in porcine coronary artery.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jan 26;555(2-3):178-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.10.035. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17113071
-
Characterization of the induction of nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase in rat aorta in organ culture.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 May;121(1):125-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701100. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9146896 Free PMC article.
-
Vasorelaxant effects of Cerebralcare Granule® are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, potassium channel opening and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):572-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.062. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24924524
Cited by
-
Terminalia fagifolia Mart. & Zucc. elicits vasorelaxation of rat thoracic aorta through nitric oxide and K+ channels dependent mechanism.Biol Open. 2019 Feb 27;8(2):bio035238. doi: 10.1242/bio.035238. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 30683674 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid vasodilation to raloxifene: role of oestrogen receptors and off-target effects.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;174(22):4201-4202. doi: 10.1111/bph.14020. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28983907 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bazedoxifene-induced vasodilation and inhibition of vasoconstriction is significantly greater than estradiol.Menopause. 2019 Feb;26(2):172-181. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001195. Menopause. 2019. PMID: 30130290 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen relaxes gastric muscle cells via a nitric oxide- and cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent mechanism: A sex-associated differential effect.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Sep;16(3):1685-1692. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6406. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30186388 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a Bradykinin B2 Partial Agonist Profile of Raloxifene in a Drug Repurposing Campaign.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 29;22(1):257. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010257. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33383825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrett‐Connor E, Bush TL (1991). Estrogen and coronary heart disease in women. JAMA 265: 1861–1867. - PubMed
-
- Barrett‐Connor E, Grady D, Sasheyi A, Anderson PW, Cox DA, Hoszowski K et al. (2002). Raloxifene and cardiovascular events in osteoporotic postmenopausal women: four‐year results from the MORE (Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation) randomized trial. JAMA 287: 847–857. - PubMed
-
- Barrett‐Connor E, Mosca L, Collins P, Geiger MJ, Grady D, Kornitzer M et al. (2006). Effects of raloxifene on cardiovascular events and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med 355: 125–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

