Histone H4 expression is cooperatively maintained by IKKβ and Akt1 which attenuates cisplatin-induced apoptosis through the DNA-PK/RIP1/IAPs signaling cascade
- PMID: 28139737
- PMCID: PMC5282510
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41715
Histone H4 expression is cooperatively maintained by IKKβ and Akt1 which attenuates cisplatin-induced apoptosis through the DNA-PK/RIP1/IAPs signaling cascade
Abstract
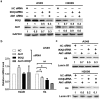
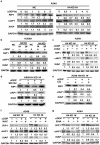
While chromatin remodeling mediated by post-translational modification of histone is extensively studied in carcinogenesis and cancer cell's response to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, little is known about the role of histone expression in chemoresistance. Here we report a novel chemoresistance mechanism involving histone H4 expression. Extended from our previous studies showing that concurrent blockage of the NF-κB and Akt signaling pathways sensitizes lung cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis, we for the first time found that knockdown of Akt1 and the NF-κB-activating kinase IKKβ cooperatively downregulated histone H4 expression, which increased cisplatin-induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells. The enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity in histone H4 knockdown cells was associated with proteasomal degradation of RIP1, accumulation of cellular ROS and degradation of IAPs (cIAP1 and XIAP). The cisplatin-induced DNA-PK activation was suppressed in histone H4 knockdown cells, and inhibiting DNA-PK reduced expression of RIP1 and IAPs in cisplatin-treated cells. These results establish a novel mechanism by which NF-κB and Akt contribute to chemoresistance involving a signaling pathway consisting of histone H4, DNA-PK, RIP1 and IAPs that attenuates ROS-mediated apoptosis, and targeting this pathway may improve the anticancer efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Fojo T. Cancer, DNA repair mechanisms, and resistance to chemotherapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 93, 1434–1436 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal B. B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: the enemy within. Cancer Cell 6, 203–208 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Caporali S. et al. AKT is activated in an ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3-related-dependent manner in response to temozolomide and confers protection against drug-induced cell growth inhibition. Mol. Pharmacol. 74, 173–183 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

