Independent movement of the voltage sensors in KV2.1/KV6.4 heterotetramers
- PMID: 28139741
- PMCID: PMC5282584
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41646
Independent movement of the voltage sensors in KV2.1/KV6.4 heterotetramers
Abstract
Heterotetramer voltage-gated K+ (KV) channels KV2.1/KV6.4 display a gating charge-voltage (QV) distribution composed by two separate components. We use state dependent chemical accessibility to cysteines substituted in either KV2.1 or KV6.4 to assess the voltage sensor movements of each subunit. By comparing the voltage dependences of chemical modification and gating charge displacement, here we show that each gating charge component corresponds to a specific subunit forming the heterotetramer. The voltage sensors from KV6.4 subunits move at more negative potentials than the voltage sensors belonging to KV2.1 subunits. These results indicate that the voltage sensors from the tetrameric channels move independently. In addition, our data shows that 75% of the total charge is attributed to KV2.1, while 25% to KV6.4. Thus, the most parsimonious model for KV2.1/KV6.4 channels' stoichiometry is 3:1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



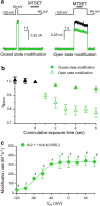

References
-
- Hille B. Ionic channels of excitable membranes. 2 edn (Sinauer Associates, 1991).
-
- Bezanilla F. The voltage sensor in voltage-dependent ion channels. Physiol. Rev. 80, 555–592 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Papazian D. M., Timpe L. C., Jan Y. N. & Jan L. Y. Alteration of voltage-dependence of Shaker potassium channel by mutations in the S4 sequence. Nature 349, 305–310 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Long S. B., Campbell E. B. & MacKinnon R.. Crystal structure of a mammalian voltage-dependent Shaker family K+ channel. Science 309, 897–903 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Seoh S. A., Sigg D., Papazian D. M. & Bezanilla F. Voltage-sensing residues in the S2 and S4 segments of the Shaker K+ channel. Neuron 16, 1159–1167 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

