Roxatidine attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation via inhibition of NF-κB and p38 MAPK activation
- PMID: 28139747
- PMCID: PMC5282503
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41721
Roxatidine attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation via inhibition of NF-κB and p38 MAPK activation
Abstract
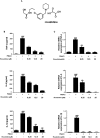
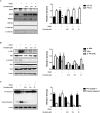
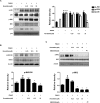
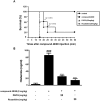
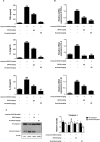
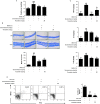
Roxatidine is an active metabolite of roxatidine acetate hydrochloride which is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that is used to treat gastric and duodenal ulcers. In this study, we investigated the anti-allergic inflammatory effects and the underlying molecular mechanism of roxatidine in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and calcium ionophore (PMACI)-stimulated human mast cells-1 (HMC-1), compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic animal model and chemical allergen-induced contact hypersensitivity (CHS) models. Roxatidine suppressed the mRNA and protein expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in PMACI-stimulated HMC-1 and compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic mice. In addition, roxatidine attenuated PMACI-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB and the phosphorylation of MKK3/6 and MK2, which are both involved in the p38 MAPK pathway. Furthermore, we observed that roxatidine suppressed the activation of caspase-1, an IL-1β converting enzyme, in PMACI-stimulated HMC-1 and compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic mice. In CHS model, roxatidine significantly reduced ear swelling, increased number of mast cells, production levels of cytokines and migration of dendritic cells. Our findings provide evidence that the anti-allergic inflammatory properties of roxatidine are mediated by the inhibition of NF-κB and caspase-1 activation, p38 MAPK pathway and mast cell-derived cytokine production. Taken together, the in vitro and in vivo anti-allergic inflammatory effects suggest a possible therapeutic application of roxatidine in allergic inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kemp S. F. & Lockey R. F. Anaphylaxis: a review of causes and mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol 110, 341–348 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Kim S. H. et al. Gallic acid inhibits histamine release and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in mast cells. Toxicological sciences: an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 91, 123–131 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Baud V. & Karin M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol 11, 372–377 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P. A. & Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science 242, 540–546 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

