Functional Outcomes of Heparin-Binding Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Growth Factor for Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations in Mice
- PMID: 28142401
- PMCID: PMC5444491
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0395
Functional Outcomes of Heparin-Binding Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Growth Factor for Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations in Mice
Abstract
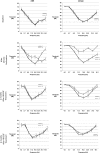
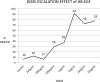
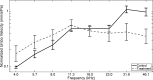
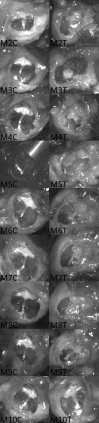
We aim to demonstrate that regeneration of chronic tympanic perforations with heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) delivered by an injectable hydrogel restored hearing to levels similar to that of nonperforated tympanic membranes. Chronic tympanic membrane perforation is currently managed as an outpatient surgery with tympanoplasty. Due to the costs of this procedure in the developed world and a lack of accessibility and resources in developing countries, there is a great need for a new treatment that does not require surgery. In this study, we show in a mouse model through measurement of auditory brainstem response and distortion product otoacoustic emissions that tympanic perforations lead to hearing loss and this can be predominantly recovered with HB-EGF treatment (5 μg/mL). Our animal model suggests a return to function between 2 and 6 months after treatment. Auditory brainstem response thresholds had returned to the control levels at 2 months, but the distortion product otoacoustic emissions returned between 2 and 6 months. We also show how the vibration characteristics of the regenerated tympanic membrane, as measured by laser Doppler vibrometry, can be similar to that of an unperforated tympanic membrane. Using the best available methods for preclinical evaluation in animal models, it is likely that HB-EGF-like growth factor treatment leads to regeneration of chronic tympanic membrane perforations and restoration of the tympanic membrane to normal function, suggesting a potential route for nonsurgical treatment.
Keywords: HB-EGF; chronic perforation; tympanic membrane; tympanic regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose the following potential conflicts of interest: Filed patents: U.S. Non Provisional No. 61/823,749, April 2014 (P.S.M, S.K., Y.Y.); and U.S. Non Provisional No. 61/810,101, April 2014 (S.K., Y.Y.).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heparin binding-epidermal growth factor-like growth factor for the regeneration of chronic tympanic membrane perforations in mice.Tissue Eng Part A. 2015 May;21(9-10):1483-94. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2014.0474. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015. PMID: 25567607 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin Binding Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Growth Factor Heals Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations With Advantage Over Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 and Epidermal Growth Factor in an Animal Model.Otol Neurotol. 2015 Aug;36(7):1279-83. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000795. Otol Neurotol. 2015. PMID: 26075672 Free PMC article.
-
In Response to: Heparin Binding-Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Growth Factor for the Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations in Mice.Tissue Eng Part A. 2016 Mar;22(5-6):568-9. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0040. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016. PMID: 26879548 No abstract available.
-
Effect of tympanic perforations on the detection of distortion-product otoacoustic emissions.Ear Nose Throat J. 2000 Aug;79(8):610-2, 614-6, 618. Ear Nose Throat J. 2000. PMID: 10969471 Review.
-
A moist edge environment aids the regeneration of traumatic tympanic membrane perforations.J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Jul;131(7):564-571. doi: 10.1017/S0022215117001001. Epub 2017 May 15. J Laryngol Otol. 2017. PMID: 28502255 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Growth Factor-Loaded Acellular Dermal Matrix/MSCs on Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations in Rats.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 6;10(7):1541. doi: 10.3390/jcm10071541. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33917576 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2 and EGF for the Regeneration of Tympanic Membrane: A Systematic Review.Stem Cells Int. 2021 Jun 29;2021:2366291. doi: 10.1155/2021/2366291. eCollection 2021. Stem Cells Int. 2021. PMID: 34306094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparin-Binding Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Growth Factor as a Critical Mediator of Tissue Repair and Regeneration.Am J Pathol. 2018 Nov;188(11):2446-2456. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30142332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locally administered heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor reduces radiation-induced oral mucositis in mice.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 15;10(1):17327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73875-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33060741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acuin J. Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Burden of Illness and Management Options. Switzerland: World Health Organisation, 2004
-
- Hong P., Bance M., and Gratzer P.F. Repair of tympanic membrane perforation using novel adjuvant therapies: a contemporary review of experimental and tissue engineering studies. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 77, 3, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Jackler R.K. A regenerative method of tympanic membrane repair could be the greatest advance in otology since the cochlear implant. Otol Neurotol 33, 289, 2012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

