Conservation and diversification of the miR166 family in soybean and potential roles of newly identified miR166s
- PMID: 28143404
- PMCID: PMC5286673
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-017-0983-9
Conservation and diversification of the miR166 family in soybean and potential roles of newly identified miR166s
Abstract
Background: microRNA166 (miR166) is a highly conserved family of miRNAs implicated in a wide range of cellular and physiological processes in plants. miR166 family generally comprises multiple miR166 members in plants, which might exhibit functional redundancy and specificity. The soybean miR166 family consists of 21 members according to the miRBase database. However, the evolutionary conservation and functional diversification of miR166 family members in soybean remain poorly understood.
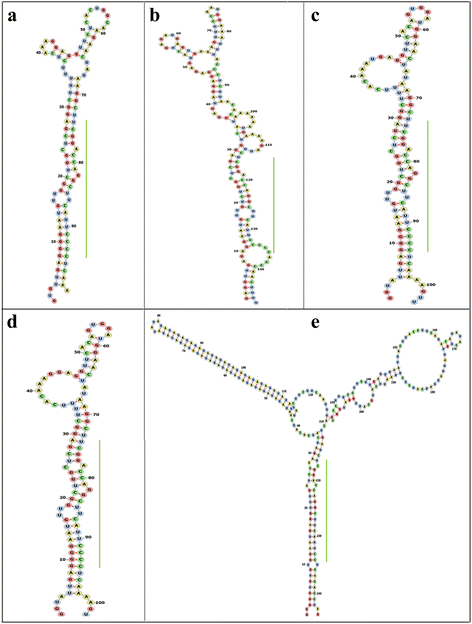
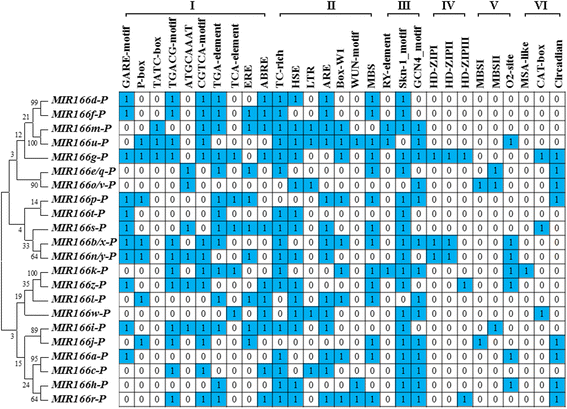
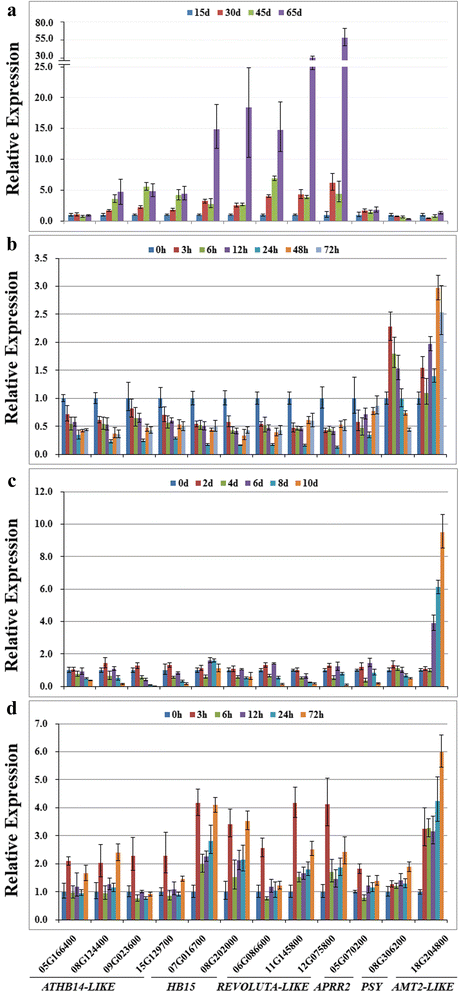
Results: We identified five novel miR166s in soybean by data mining approach, thus enlarging the size of miR166 family from 21 to 26 members. Phylogenetic analyses of the 26 miR166s and their precursors indicated that soybean miR166 family exhibited both evolutionary conservation and diversification, and ten pairs of miR166 precursors with high sequence identity were individually grouped into a discrete clade in the phylogenetic tree. The analysis of genomic organization and evolution of MIR166 gene family revealed that eight segmental duplications and four tandem duplications might occur during evolution of the miR166 family in soybean. The cis-elements in promoters of MIR166 family genes and their putative targets pointed to their possible contributions to the functional conservation and diversification. The targets of soybean miR166s were predicted, and the cleavage of ATHB14-LIKE transcript was experimentally validated by RACE PCR. Further, the expression patterns of the five newly identified MIR166s and 12 target genes were examined during seed development and in response to abiotic stresses, which provided important clues for dissecting their functions and isoform specificity.
Conclusion: This study enlarged the size of soybean miR166 family from 21 to 26 members, and the 26 soybean miR166s exhibited evolutionary conservation and diversification. These findings have laid a foundation for elucidating functional conservation and diversification of miR166 family members, especially during seed development or under abiotic stresses.
Keywords: Evolutionary conservation and diversification; Gene expression pattern; Promoter analysis; Soybean; miR166 family.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Phylogenetic analysis reveals conservation and diversification of micro RNA166 genes among diverse plant species.Genomics. 2014 Jan;103(1):114-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24275521
-
Conservation and Diversity of miR166 Family Members From Highbush Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) and Their Potential Functions in Abiotic Stress.Front Genet. 2022 May 16;13:919856. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.919856. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35651935 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of action of microRNA166 on nitric oxide in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under drought stress.BMC Genomics. 2024 Mar 28;25(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10095-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38549050 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis of carbonic anhydrases genes in soybean (Glycine max).Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Jan 14;23(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-00966-9. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36639600 Review.
-
MicroRNA166: Old Players and New Insights into Crop Agronomic Traits Improvement.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;15(7):944. doi: 10.3390/genes15070944. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of VvmiR166s-Target Modules and Their Interaction Pathways in Modulation of Gibberellic-Acid-Induced Grape Seedless Berries.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 14;24(22):16279. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216279. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003470 Free PMC article.
-
Highly preserved roles of Brassica MIR172 in polyploid Brassicas: ectopic expression of variants of Brassica MIR172 accelerates floral transition.Mol Genet Genomics. 2018 Oct;293(5):1121-1138. doi: 10.1007/s00438-018-1444-3. Epub 2018 May 11. Mol Genet Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29752548
-
Edible plant-derived exosomal microRNAs: Exploiting a cross-kingdom regulatory mechanism for targeting SARS-CoV-2.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;414:115425. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115425. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33516820 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of microRNAs and histone modifications in enhancing stress tolerance in soybean and their applications in molecular breeding.Breed Sci. 2025 Mar;75(1):67-78. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.24039. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Breed Sci. 2025. PMID: 40585574 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Expression Analysis of the Nucleotidyl Transferase Protein (NTP) Family in Soybean (Glycine max) under Various Abiotic Stresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 17;25(2):1115. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021115. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256188 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

