Oxidative DNA damage is epigenetic by regulating gene transcription via base excision repair
- PMID: 28143930
- PMCID: PMC5347626
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1619809114
Oxidative DNA damage is epigenetic by regulating gene transcription via base excision repair
Abstract
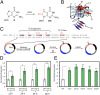
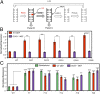
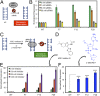
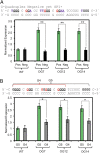
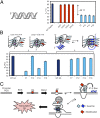
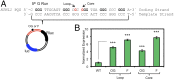
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have emerged as important cellular-signaling agents for cellular survival. Herein, we demonstrate that ROS-mediated oxidation of DNA to yield 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (OG) in gene promoters is a signaling agent for gene activation. Enhanced gene expression occurs when OG is formed in guanine-rich, potential G-quadruplex-forming sequences (PQS) in promoter-coding strands, initiating base excision repair (BER) by 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (OGG1), yielding an abasic site (AP). The AP enables melting of the duplex to unmask the PQS, adopting a G-quadruplex fold in which apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) binds, but inefficiently cleaves, the AP for activation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or endonuclease III-like protein 1 (NTHL1) genes. These details were mapped via synthesis of OG and AP analogs at single-nucleotide precision within the promoter of a luciferase reporter system. The reporters were analyzed in human and mouse cells while selectively knocking out or down critical BER proteins to identify the impact on luciferase expression. Identification of the oxidatively modified DNA base OG to guide BER activity in a gene promoter and impact cellular phenotype ascribes an epigenetic role to OG.
Keywords: G-quadruplex; base excision repair; epigenetics; gene regulation; oxidative damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
G-quadruplex-forming promoter sequences enable transcriptional activation in response to oxidative stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 14;114(11):2788-2790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701244114. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28265096 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hailer-Morrison MK, Kotler JM, Martin BD, Sugden KD. Oxidized guanine lesions as modulators of gene transcription. Altered p50 binding affinity and repair shielding by 7,8-dihydro-8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine lesions in the NF-kappaB promoter element. Biochemistry. 2003;42(32):9761–9770. - PubMed
-
- Ramon O, et al. Effects of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine on the binding of the transcription factor Sp1 to its cognate target DNA sequence (GC box) Free Radic Res. 1999;31(3):217–229. - PubMed
-
- Moore SP, Toomire KJ, Strauss PR. DNA modifications repaired by base excision repair are epigenetic. DNA Repair (Amst) 2013;12(12):1152–1158. - PubMed
-
- Tornaletti S, Maeda LS, Kolodner RD, Hanawalt PC. Effect of 8-oxoguanine on transcription elongation by T7 RNA polymerase and mammalian RNA polymerase II. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3(5):483–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

