Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Levels During Pneumoperitoneum
- PMID: 28144124
- PMCID: PMC5266513
- DOI: 10.4293/JSLS.2016.00091
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Levels During Pneumoperitoneum
Abstract
Background and objectives: A temporary deterioration in renal function during pneumoperitoneum has been reported, but the extent is not known. A new marker for the early detection of renal injury, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), has been shown to increase in various conditions that affect renal function. This study was conducted to explore detrimental effects of pneumoperitoneum in laparoscopic surgery on renal function by studying levels of urinary NGAL (uNGAL).
Methods: Thirty-two women scheduled to undergo laparoscopic surgery in a gynecology clinic were recruited. NGAL was measured in urine collected at the beginning (0 h) and at 2 and 24 hours after the initiation of surgery. Hemodynamic parameters were analyzed immediately after intubation and before desufflation.
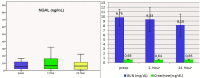
Results: Levels of uNGAL increased from 5.45 ng/mL at 0 hours to 6.35 ng/mL at 2 hours and to 6.05 ng/mL at 24 h; however, there was no significant change in uNGAL levels at the collection time points. Intraoperative oliguria was observed in all cases, and the severity increased with the duration of surgery. uNGAL levels did not correlate with the duration of surgery or pneumoperitoneum.
Conclusion: In patients with normal renal functions, pneumoperitoneum results in transient oliguria without any early renal damage, as indicated by nonsignificant changes in uNGAL levels.
Keywords: Laparoscopy; Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin; pneumoperitoneum; renal function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as an Early Marker of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy After Elective Invasive Cardiac Procedures.Clin Cardiol. 2016 Aug;39(8):464-70. doi: 10.1002/clc.22551. Epub 2016 May 13. Clin Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27175937 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective assessment of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipoprotein in living kidney donors: toward understanding differences between chronic kidney diseases of surgical and medical origin.BJU Int. 2019 May;123(5):869-876. doi: 10.1111/bju.14592. Epub 2018 Nov 8. BJU Int. 2019. PMID: 30347133
-
Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as Predictor of Short- or Long-Term Outcomes in Cardiac Surgery Patients.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2015 Dec;29(6):1480-8. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2015.05.060. Epub 2015 May 8. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2015. PMID: 26296821
-
Quantification of NGAL in Urine of Endurance Cycling Athletes.J Phys Act Health. 2018 Sep 1;15(9):679-682. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2017-0496. Epub 2018 Aug 1. J Phys Act Health. 2018. PMID: 30068247 Review.
-
Renal implications of pneumoperitoneum in laparoscopic surgery: mechanisms, risk factors, and preventive strategies.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2024 Dec;77(6):575-586. doi: 10.4097/kja.24011. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38664893 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of pneumoperitoneum on kidney injury biomarkers: A randomized clinical trial.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 19;16(2):e0247088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247088. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33606739 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Koivusalo AM, Kellokumpu I, Ristkari S, Lindgren L. Splanchnic and renal deterioration during and after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a comparison of the carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum and the abdominal wall lift method. Anesth Analg. 1997;85:886–891. - PubMed
-
- Demyttenaere S, Feldman LS, Fried GM. Effect of pneumoperitoneum on renal perfusion and function: a systematic review. Surg Endosc. 2007;21:152–160. - PubMed
-
- Kuwabara T, Mori K, Mukoyama M, et al. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels reflect damage to glomeruli, proximal tubules, and distal nephrons. Kidney Int. 2009;75:285–294. - PubMed
-
- Moore E, Bellomo R, Nichol A. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury in anesthesia, intensive care and major surgery: from the bench to clinical research to clinical practice. Minerva Anesthesiol. 2010;76:425–440. - PubMed
-
- Thurman JM, Parikh CR. Peeking into the black box: new bio-markers for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2008;73:379–381. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous