Clinical Manifestations in 82 Neurobrucellosis Patients from Kosovo
- PMID: 28144188
- PMCID: PMC5239658
- DOI: 10.5455/msm.2016.28.408-411
Clinical Manifestations in 82 Neurobrucellosis Patients from Kosovo
Abstract
Background: Central nervous system involvement is a serious complication of brucellosis with various incidence and various clinical presentations.
Patients and methods: Hospitalized patients in University Clinical Centre, Clinic for Infectious diseases in Prishtina, with laboratory-confirmed brucellosis, were analyzed, a brucellosis-endemic region. Among the 648 confirmed cases with brucellosis during the period 1991- 2013, 82 patients (12.65%) were diagnosed with neurobrucellosis. The clinical manifestations in patients with neurobrucellosis were evaluated and compared with brucellosis patients.
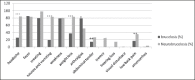
Results: The major presentations among the brucellosis patients were headache, fever, sweating, nausea, weight loss and arthralgia, while from CNS predominant complains were: headache, vomiting, tremor, low back pain, hearing loss and visual disturbance. The mean age of 82 neurobrucellosis patients was 31.46 years with age distribution 12-71 years, from them 5 (6.1%), younger than 16 years, with a non-significant predominance of women (53.65%). The most common neurological findings were radiculopathies of legs (41.46%) neck rigidity (46.34%), agitation (25,6%), behavioral disorders (18.3%), disorientation (19.5%) and stroke (1.22%). Cranial nerves were involved in 20 of 82 patients (24.4%). Neurological consequences were evidenced in 5 (6.1%) patients. Three patients leave hospital with consequences of peripheral facial paresis, two with sensorineural hearing loss and one with left hemiparesis. Headache, nausea and vomiting and weight loss are significantly (p<0.001) more frequent complains in neurobrucellosis patients compare to patients with brucellosis. On the other hand, as regard to the physical findings and complications, meningeal signs and splenomegaly are significantly more frequent in neurobrucellosis (p<0.01) whereas the hepatomegaly and lymphadenopathy were more frequent (p<0.01) in brucellosis patients. Different significant correlations were observed among specific complains too.
Conclusions: Our findings in regard to the specific associations of physical and clinical features in brucellosis patients in Kosovo, may serve as an indication for neurobrucellosis. In endemic areas for brucellosis patients complaining in radiculopathies, persistent headache, facial palsy, hearing loss or presenting stroke without risk factors, should be considered for screening for neurobrucellosis.
Keywords: Brucellosis; Clinical manifestations; Kosovo; Neurobrucellosis.
Conflict of interest statement
• Conflict of interest: none declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neurobrucellosis: clinical and diagnostic features.Clin Infect Dis. 2013 May;56(10):1407-12. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit072. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Clin Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23446629
-
Overview of neurobrucellosis: a pooled analysis of 187 cases.Int J Infect Dis. 2009 Nov;13(6):e339-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2009.02.015. Epub 2009 May 9. Int J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19428283 Review.
-
Neurobrucellosis: clinical, diagnostic, therapeutic features and outcome. Unusual clinical presentations in an endemic region.Braz J Infect Dis. 2011 Jan-Feb;15(1):52-9. Braz J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21412590
-
Evaluation of children with neurobrucellosis.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2012;113(7):424-30. doi: 10.4149/bll_2012_096. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2012. PMID: 22794518
-
Evaluation of clinical, diagnostic features and therapeutic outcome of neurobrucellosis: a case series and review of literature.Int J Neurosci. 2022 Nov;132(11):1080-1090. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1860969. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Int J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 33287603 Review.
Cited by
-
The research trend on neurobrucellosis over the past 30 years (1993-2023): a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Sep 23;15:1349530. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1349530. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39381075 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobrucellosis with ischemic stroke and spinal cord involvement: a case report.BMC Neurol. 2021 Mar 20;21(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02155-2. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33743640 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical treatment of the lower cervical brucellosis with osteoporosis in the northwest region of China: review of 22 cases.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Feb 15;14(2):909-917. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35273694 Free PMC article.
-
Motor polyradiculoneuropathy as an unusual presentation of neurobrucellosis: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 May 14;24(1):491. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09365-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38745172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurobrucellosis: the great mimicker.Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2022 Apr 8;55:e05672021. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0567-2021. eCollection 2022. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2022. PMID: 35416876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [accessed April 2009]. Available at: www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dbmd/diseaseinfo/brucellosis _g.htm#-howcommon .
-
- Buzgan T, Karahocagil MK, Irmak H, Baran AI, Karsen H, Evirgen O, Akdeniz H. Clinical manifestations and complifications in 1028 cases of brucellosis:a retrospective evaluation and review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:e469–78. - PubMed
-
- Gul HC, Erdem H, Gorenek L, Ozdag MF, Kalpakci Y, Avci IY, et al. Management of neurobrucellosis:an assessment of 11 cases. Intern Med. 2008;47:995–1001. - PubMed
-
- Yetkin MA, Bulut C, Erdinc FS, Oral B, Tulek N. Evaluation of the clinical presentations in neurobrucellosis. Int J Infect Dis. 2006;10:446–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
