Functional Disorders of Constipation: Paradoxical Puborectalis Contraction and Increased Perineal Descent
- PMID: 28144209
- PMCID: PMC5179279
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1593430
Functional Disorders of Constipation: Paradoxical Puborectalis Contraction and Increased Perineal Descent
Abstract
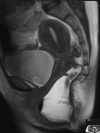
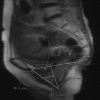
Paradoxical puborectalis contraction (PPC) and increased perineal descent (IPD) are subclasses of obstructive defecation. Often these conditions coexist, which can make the evaluation, workup, and treatment difficult. After a thorough history and examination, workup begins with utilization of proven diagnostic modalities such as cinedefecography and anal manometry. Advancements in technology have increased the surgeon's diagnostic armamentarium. Biofeedback and pelvic floor therapy have proven efficacy for both conditions as first-line treatment. In circumstances where PPC is refractory to biofeedback therapy, botulinum toxin injection is recommended. Historically, pelvic floor repair has been met with suboptimal results. In IPD, surgical therapy now is directed toward the potentially attendant abnormalities such as rectoanal intussusception and rectal prolapse. When these associated abnormalities are not present, an ostomy should be considered in patients with IPD as well as medically refractory PPC.
Keywords: biofeedback; descending perineum syndrome; dyssynergic defecation; increased perineal descent; obstructive defecation syndrome; paradoxical puborectalis contraction.
Figures
References
-
- Lembo A, Camilleri M. Chronic constipation. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(14):1360–1368. - PubMed
-
- Longstreth G F, Thompson W G, Chey W D, Houghton L A, Mearin F, Spiller R C. Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(5):1480–1491. - PubMed
-
- Rao S S. Dyssynergic defecation. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2001;30(1):97–114. - PubMed
-
- Rao S S, Welcher K D, Leistikow J S. Obstructive defecation: a failure of rectoanal coordination. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93(7):1042–1050. - PubMed
-
- Altomare D F, Spazzafumo L, Rinaldi M, Dodi G, Ghiselli R, Piloni V. Set-up and statistical validation of a new scoring system for obstructed defaecation syndrome. Colorectal Dis. 2008;10(1):84–88. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

