The Effect of Aerobic Exercise Training on Plasma Apelin Levels and Pain Threshold in T1DM Rats
- PMID: 28144460
- PMCID: PMC5253213
- DOI: 10.5812/ircmj.31737
The Effect of Aerobic Exercise Training on Plasma Apelin Levels and Pain Threshold in T1DM Rats
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus (types 1 and 2) leads to secondary complications such as neuropathy, which reduce a patient's quality of life. Apelin and its receptor, APJ, have been shown to have antinociceptive effects and to decrease blood glucose levels.
Objectives: The present experimental study was conducted in Iran and investigated the role of apelin, which is used to manage type 1 diabetes mellitus, during exercise training.
Materials and methods: Male Wistar rats (n = 36) were assigned by simple random allocation to six groups (n = 6): non-diabetic (ND), diabetic (D), sedentary non-diabetic (SND), sedentary diabetic (SD), exercise non-diabetic (END), and exercise diabetic (ED). Diabetes was induced by a single subcutaneous injection of streptozotocin (50 mg/kg). Exercise training consisted of treadmill running 60 minutes/day × 5 days/week for 10 weeks. The tail-flick test was used to assess the thermal pain threshold, and an apelin enzyme immunoassay kit was utilized to assess plasma apelin levels.
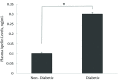
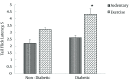
Results: Plasma apelin level was higher (0.3 vs. 0.1, P < 0.0001) and the tail-flick latency was lower (2.2 vs. 3.8, P < 0.0001) in the D group than in the ND group. After the training program, plasma apelin levels decreased in the exercise groups, and the tail-flick latency increased in the ED group. No correlation was found between apelin blood concentrations and tail-flick latency following the training program in the ED group.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that apelin does not play any significant role in regulating the pain threshold in type 1 diabetes mellitus during exercise training.
Keywords: Apelin Protein; Exercise; Pain Threshold; Rat; Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of exercise training on adipose tissue apelin expression in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats.Gene. 2018 Jul 1;662:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29626513
-
The role of resistance and aerobic exercise training on insulin sensitivity measures in STZ-induced Type 1 diabetic rodents.Metabolism. 2013 Oct;62(10):1485-94. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.05.012. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23810201
-
Comparing High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Continuous Training on Apelin, APJ, NO, and Cardiotrophin-1 in Cardiac Tissue of Diabetic Rats.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Aug 27;2020:1472514. doi: 10.1155/2020/1472514. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32908933 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training promotes expression of apelin and APJ of cardiovascular tissues in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Life Sci. 2006 Aug 15;79(12):1153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.03.040. Epub 2006 Apr 15. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16674982
-
The glucoregulatory response to high-intensity aerobic exercise following training in rats with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes mellitus.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016 Jun;41(6):631-9. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0558. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016. PMID: 27175938
Cited by
-
The function of previously unappreciated exerkines secreted by muscle in regulation of neurodegenerative diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jan 5;16:1305208. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1305208. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38249295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
