Effect of Vocalization of the Holy Quran With and Without Translation on Pregnancy Outcomes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 28144462
- PMCID: PMC5253461
- DOI: 10.5812/ircmj.35421
Effect of Vocalization of the Holy Quran With and Without Translation on Pregnancy Outcomes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: During recent decades, research in Iran in the area of the Quran and medical science has been seriously engaged in. With respect to the tendency toward spirituality and alternative medicine, we tried to find other aspects of the influence of the Quran.
Objectives: This study aimed to determine the effect of vocalizations of the Holy Quran with and without translation on the consequences of pregnancy (the prevalence of preterm delivery, caesarean delivery, and neonatal anthropometric indices) in women admitted to health care centers in Urmia, Iran.
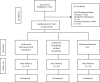
Materials and methods: This was a three-armed parallel-group randomized clinical trial in which 168 pregnant women (25-28 weeks) in their first and second pregnancies were divided into three groups of 56 (Holy Quran with translation, Holy Quran without translation, and control group) by randomized blocking. The intervention was implemented once a week for three weeks in the health center, and on other days of the week, the participants listened at home to a CD they were given. The intervention and the control groups all received routine pregnancy care once a week. These mothers were tracked during their labor. Outcomes including gestational age at delivery, delivery type, and neonatal anthropometric indices were recorded based on the mother's records.
Results: There was no statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of demographic and obstetric characteristics before the intervention. In comparison with the control group, the probability of preterm delivery was lower in the Holy Quran with translation group (odds ratio: 0.3, CI 95%: 0.1-1.2) and in the Holy Quran without translation group (0.6, 0.2-1.9) as compared to the control group. However, this difference was not statistically significant. Similarly, the probability of caesarean delivery was lower in the Holy Quran with translation group (0.6, 0.3-1.4) and the Holy Quran without translation group (0.5, 0.2-1.2) as compared to the control group. Based on one-way ANOVA, there was no statistically significant difference between the study groups regarding the infants' anthropometric indices.
Conclusions: Based on the results of this study, despite the lower prevalence of preterm labor and caesarean section in the intervention groups as compared to the control group, no statistically significant effect was seen. This was apparently due to the small sample size.
Keywords: Anthropometric Indices; Caesarean Section; Neonatal, Preterm Labor; Quran.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests:The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
The effect of the holy Quran recitation and listening on anxiety, stress, and depression: A scoping review on outcomes.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 7;6(12):e1751. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1751. eCollection 2023 Dec. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38078304 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Holly Quran Voice With and Without Translation on Stress, Anxiety and Depression During Pregnancy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Relig Health. 2020 Feb;59(1):544-554. doi: 10.1007/s10943-017-0417-x. J Relig Health. 2020. PMID: 28560489 Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of the Holy Quran Recitation on Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients in Iran: A Randomized Clinical Trial.J Relig Health. 2024 Dec;63(6):4826-4839. doi: 10.1007/s10943-023-01989-z. Epub 2024 Jan 11. J Relig Health. 2024. PMID: 38206560 Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Listening to Holy Quran Recitation on Anxiety: A Systematic Review.Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2018 Nov-Dec;23(6):411-420. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.IJNMR_173_17. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2018. PMID: 30386389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Listening to Holy Quran Recital on Pain and Length of Stay Post-CABG: A Randomized Control Trial.Crit Care Res Pract. 2023 Nov 6;2023:9430510. doi: 10.1155/2023/9430510. eCollection 2023. Crit Care Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37965250 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of the holy Quran recitation and listening on anxiety, stress, and depression: A scoping review on outcomes.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 7;6(12):e1751. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1751. eCollection 2023 Dec. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38078304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghanei M. Quran: Healer and preservation factor from diseases. 2012;1(2):1–3.
-
- Makarem S. Quran kareem. Translated to persian. Tehran: Hystory and Islamic Maaref pub; 2001.
-
- Khatoni A. The effect of reciting the quran on anxiety of patients hospitalized in the cardiac intensive care unit of the selected hospitals in tehran. 1997;1(39):22–4.
-
- Almerud S, Petersson K. Music therapy--a complementary treatment for mechanically ventilated intensive care patients. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2003;19(1):21–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources