Outcome Analysis of Intra-Articular Scapula Fracture Fixation with Distal Radius Plate: A Multicenter Prospective Study
- PMID: 28144606
- PMCID: PMC5251347
- DOI: 10.5812/atr.36406
Outcome Analysis of Intra-Articular Scapula Fracture Fixation with Distal Radius Plate: A Multicenter Prospective Study
Abstract
Background: Scapula fractures occur in approximately 1% of all fractures and constitute about 3% - 5% of all injuries of the shoulder joint.
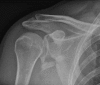
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the clinical outcomes of 20 surgically treated patients with displaced glenoid fractures after stabilization with distal radius plate.
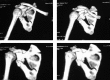
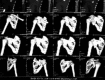
Methods: Between 2012 and 2015, at 2 centers (HMCH & SHCE) of Bhubaneswar Odisha, we stabilized 20 scapular intra-articular fractures surgically with distal radius locking plate and studied the outcome of the surgeries. The outcome of the 20 fractures was determined using the Constant and Murley score. Both shoulders were assessed and the score on the injured side was given as a percentage of that on the uninjured side.
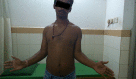
Results: The median score was 88% (mean 65%, range 30 to 100). The median score for strength was 21/25 (mean 19, range 0 to 25) and that for pain 11/15 (mean 11, range 5 to 15). The median functional score was 16/20 (mean 15, range 0 to 20). The mean range of active abduction of the shoulder was 135° (20 to 180), the mean range of flexion 138° (20 to 180) and the mean range of external rotation 38° (0 to 100). Five patients showed excellent result; 11 patients showed good result; three patients showed fair result and one patient had poor outcome according to the Constant-Murley score. A superficial infection settled with antibiotics after operation in one patient whose score at final follow-up was 96%. In one patient, delayed healing was reported because of infection. One patient with stiffness of the shoulder at six weeks underwent manipulation under anesthesia with a follow-up score of 81%.
Conclusions: Various fixation modalities have been described in the literature, however fixation of intra-articular fracture of glenoid with distal radius locking plate for articular reconstruction in the presented series provides good functional outcome with early restoration of the range of motion of the shoulder.
Keywords: Distal Radius Plate; Fall From Height; Intra Articular Glenoid; Intra Articular Scapula; Scapula Fracture; Trauma Glenoid.
Figures



References
-
- Ada JR, Miller ME. Scapular fractures. Analysis of 113 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(269):174–80. - PubMed
-
- Euler E, Habermeyer P, Kohler W, Schweiberer L. [Scapula fractures--classification and differential therapy]. Orthopade. 1992;21(2):158–62. - PubMed
-
- Ideberg R, Grevsten S, Larsson S. Epidemiology of scapular fractures. Incidence and classification of 338 fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 1995;66(5):395–7. - PubMed
-
- Kavanagh BF, Bradway JK, Cofield RH. Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced intra-articular fractures of the glenoid fossa. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(4):479–84. - PubMed
-
- McGinnis M, Denton JR. Fractures of the scapula: a retrospective study of 40 fractured scapulae. J Trauma. 1989;29(11):1488–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
