A defined syphilis vaccine candidate inhibits dissemination of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum
- PMID: 28145405
- PMCID: PMC5296639
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14273
A defined syphilis vaccine candidate inhibits dissemination of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum
Abstract
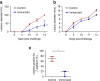
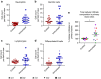
Syphilis is a prominent disease in low- and middle-income countries, and a re-emerging public health threat in high-income countries. Syphilis elimination will require development of an effective vaccine that has thus far remained elusive. Here we assess the vaccine potential of Tp0751, a vascular adhesin from the causative agent of syphilis, Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Tp0751-immunized animals exhibit a significantly reduced bacterial organ burden upon T. pallidum challenge compared with unimmunized animals. Introduction of lymph nodes from Tp0751-immunized, T. pallidum-challenged animals to naive animals fails to induce infection, confirming sterile protection. These findings provide evidence that Tp0751 is a promising syphilis vaccine candidate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of antibodies induced by immunization with the syphilis vaccine candidate Tp0751.Vaccine. 2025 Mar 19;50:126804. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2025.126804. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Vaccine. 2025. PMID: 39908783
-
Evidence that immunization with TP0751, a bipartite Treponema pallidum lipoprotein with an intrinsically disordered region and lipocalin fold, fails to protect in the rabbit model of experimental syphilis.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Sep 16;16(9):e1008871. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008871. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32936831 Free PMC article.
-
Non-pathogenic Borrelia burgdorferi expressing Treponema pallidum TprK and Tp0435 antigens as a novel approach to evaluate syphilis vaccine candidates.Vaccine. 2019 Mar 22;37(13):1807-1818. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.02.022. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 30797635 Free PMC article.
-
Syphilis Vaccine Development: Requirements, Challenges, and Opportunities.Sex Transm Dis. 2018 Sep;45(9S Suppl 1):S17-S19. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000831. Sex Transm Dis. 2018. PMID: 29528992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress towards an effective syphilis vaccine: the past, present and future.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2006 Feb;5(1):67-80. doi: 10.1586/14760584.5.1.67. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2006. PMID: 16451109 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylated vimentin-triggered fibronectin matrix disaggregation enhances the dissemination of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum across the microvascular endothelial barrier.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 3;20(9):e1012483. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012483. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39226326 Free PMC article.
-
De novo identification of bacterial antigens of a clinical isolate by combining use of proteosurfaceomics, secretomics, and BacScan technologies.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 30;14:1274027. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274027. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38098490 Free PMC article.
-
The pan-genome of Treponema pallidum reveals differences in genome plasticity between subspecies related to venereal and non-venereal syphilis.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jan 10;21(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6430-6. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31924165 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of Preclinical Studies Evaluating Nanoparticle-Based Vaccines Against Non-Viral Sexually Transmitted Infections.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 24;12:768461. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.768461. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in the development of nucleic acid vaccines for syphilis prevention and control.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug 1;19(2):2234790. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2234790. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37538024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization, Department of Reproductive Health and Research. Prevalence and incidence of selected sexually transmitted infections Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, syphilis and Trichomonas vaginalis: methods and results used by WHO to generate 2005 estimates http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/rtis/9789241502450/en/ (2011).
-
- Petersen J., Gibin M., Sile B. & Simms I. Identifying and interpreting spatiotemporal variation in diagnoses of infectious syphilis among men, England: 2009 to 2013. Sex. Transm. Infect. 92, 380–386 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

