The antibacterial activities of aditoprim and its efficacy in the treatment of swine streptococcosis
- PMID: 28145487
- PMCID: PMC5286432
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41370
The antibacterial activities of aditoprim and its efficacy in the treatment of swine streptococcosis
Abstract
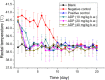
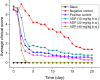
Aditoprim (ADP) has potential use as an antimicrobial agent in animals. However, its pharmacodynamic properties have not been systematically studied yet. In this study, the in vitro antibacterial activities of ADP and its main metabolites were assayed, and the in vivo antibacterial efficacy of ADP for the treatment of swine streptococcosis was evaluated. It was shown that Salmonella and Streptococcus from swine, Escherichia coli and Salmonella from chickens, E. coli, Streptococcus, Mannheimia, Pasteurella from calves, Streptococcus and Mannheimia from sheep, and E. coli, Flavobacterium columnare, Acinetobacter baumannii and Yersinia ruckeri from fishes were highly susceptible to ADP. Haemophilus parasuis from swine, Staphylococcus aureus, Aeromonas punctate, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Streptococcus agalactiae from fishes, and Klebsiella from calves and sheep showed moderate susceptibility to ADP, whereas E. coli, Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia, Pasteurella, S. aureus, Clostridium perfringens from swine, S. aureus, C. perfringens from chickens, and S. aureus from calves were resistant to ADP. The main metabolites of ADP showed equal activity to that of their parent compound, and the prevention and therapeutic dosages of ADP recommended for swine streptococcosis were 10 and 20~40 mg/kg b.w., respectively. This study firstly showed that ADP had strong antibacterial activity and had potential to be used as a single drug in the treatment of bacterial infectious diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Then R. L. & Keller M. Properties of aditoprim, a new antibacterial dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor. Zentralbl. Veterinarmed. B 35, 114–120 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Bushby S. R. M. Trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole: in-vitro microbiological aspects. J. Infect. Dis. 128 (suppl), 442–462 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Bach M. C., Finland M., Gold O. & Wilcox C. Susceptibility of recently isolated pathogenic bacteria to trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole separately and combined. J. Infect. Dis. 128 (suppl), 508–533 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Japan Cooperative Bacteriological Study Group for Co-Trimoxarole. Analysis of in-vitro antimicrobial activities of the combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole on clinical isolates in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 128 (suppl), 502–507 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Ascalone V., Jordan J. C. & Ludwig B. M. Determination of aditoprim, a new dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, in the plasma of cows and pigs. J. Chromatogr. 383, 111–118 (1986). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

